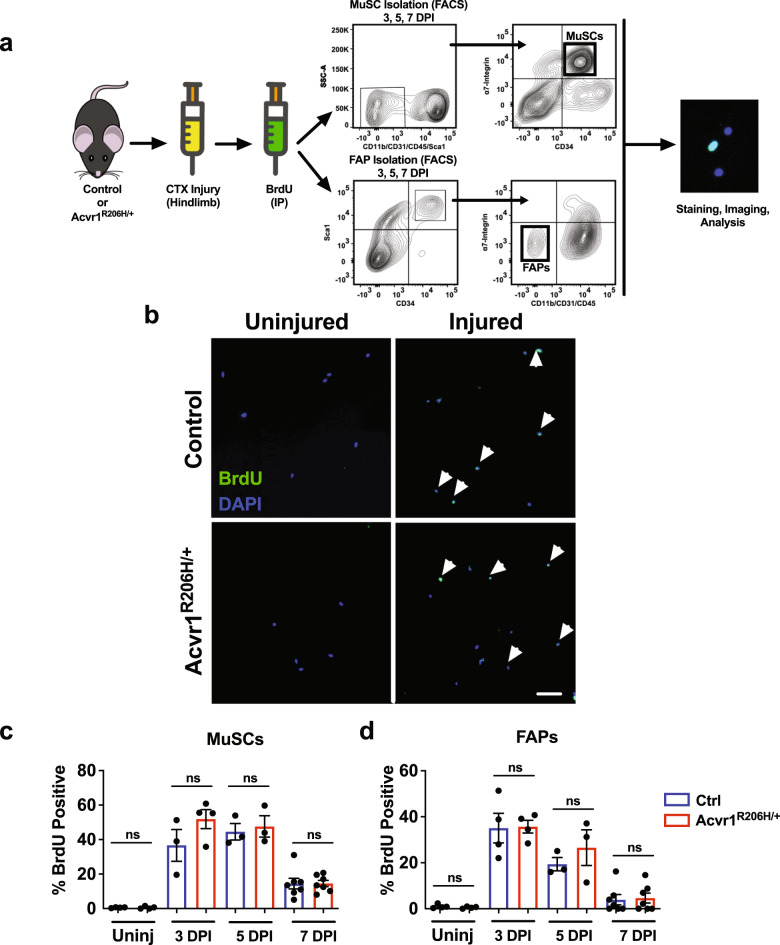
Fig. 2. In vivo proliferation capability is similar between control and Acvr1R206H/+ MuSCs and FAPs.
a Schematic representation of in vivo proliferation assay. The Tibialis Anterior and Gastrocnemius muscles of mice (2 month old) were injured with CTX and intraperitoneally injected with BrdU to label proliferating cells 24 h before isolation. MuSCs and FAPs were isolated by fluorescent activated cell sorting (FACS) based on the cell surface markers CD34 and α7-integrin for MuSCs and Sca1, CD34, and lack of α7-integrin for FAPs. b Representative images of BrdU-stained (green) isolated control and Acvr1R206H/+ cells from uninjured and injured muscle. Scale bar = 50 μm. c Quantification of the percent of BrdU+ MuSCs and d FAPs. Graphs represent the mean ± SEM. n ≥ 3 mice for each group; N > 300 MuSCs or FAPs per timepoint and genotype were analyzed. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA; ns not significant.