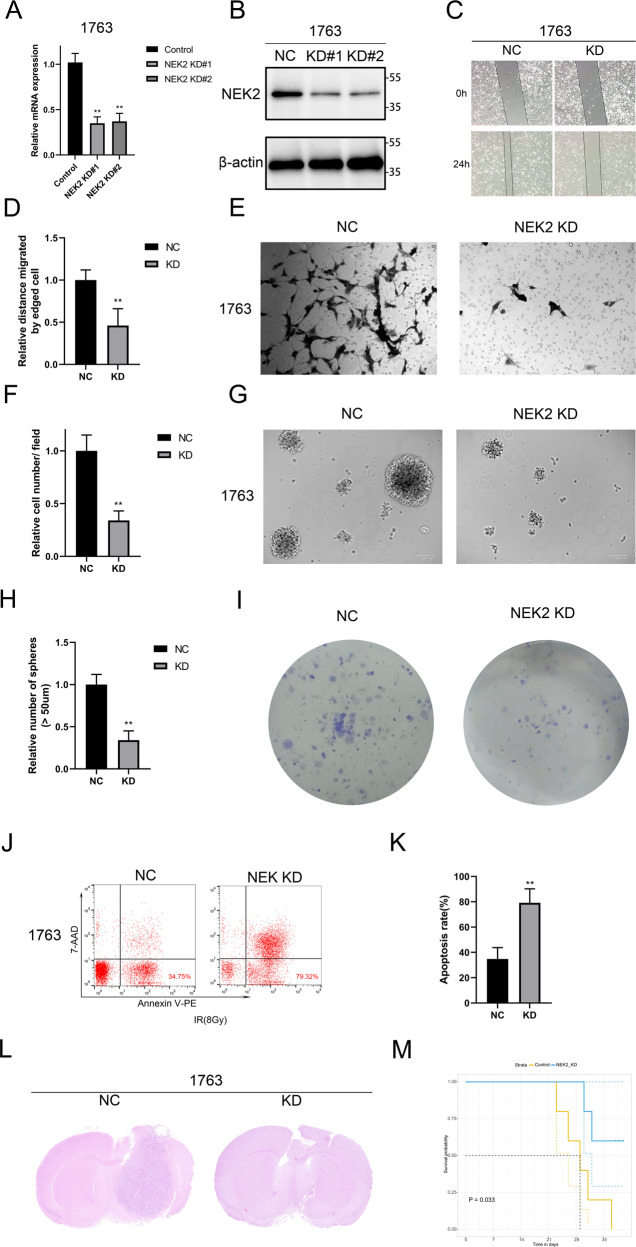
Fig. 2. NEK2 knockdown reduced the malignancy of GBM cells both in vivo and vitro.
A qRT-PCR analysis for the mRNA expression of NEK2 in 1763 cells transduced with lentiviral shNEK2 #1 and #2, and control group. B Western blot analysis for detecting the NEK2 protein expression in 1763 cell line transduced with lentiviral shNEK2 #1 and #2, and control. C, D Wound healing assays for exploring the effect of NEK2 knockdown on tumor malignancy in GBM cells. E, F Matrigel invasion assays were used to verify the inhibition of NEK2 knockdown on tumor invasive ability. G, H Sphere formation assays were performed to detect the sphere formation efficiency of NEK2 knockdown cells and control cells. I Colony formation assays to verify the effect of NEK2 knockdown on the proliferation of GBM. J, K Flow cytometry analysis using Annexin V and Propidium Iodide for apoptotic ratio analysis in 1763 cells transduced with lentiviral shNEK2 and negative control. L Representative H&E-stained images of mouse brain sections after the intracranial transplantation. Scale bars: 3 mm. M Kaplan-Meier survival curves of the xenograft mice in control group and NEK2 knockdown group (P = 0.033, with log-rank test). All data were presented as the mean ± SD of triplicate independent experiments.