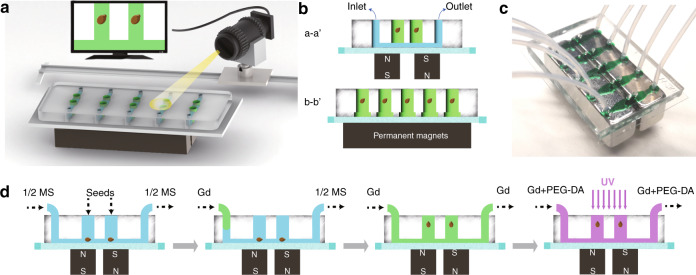
Fig. 1. Schematic illustration of the experimental setup and procedures.
a On-site monitoring of Arabidopsis seeds by implementing a camera on a slide toward the microfluidic device. b Schematic of the microfluidic chip with five channels for seed cultivation. Each channel (10 mm in length, 2 mm in width, and 100 μm in height) has two cultivation reservoirs (1000 μm in diameter, 2 mm in depth) that are cut through the PDMS layer. c Photograph of the microfluidic negative magnetophoresis platform. Two permanent magnets are assembled beneath the glass substrate, and the inner edges are aligned to the cultivation reservoirs. d The experimental procedures. First, the seeds are put into the cultivation reservoirs, and the culture medium is injected into microchannels. Second, the culture medium was replaced by Gd3+ solution. Third, the seeds are lifted and maintained at the position by negative magnetophoresis. Finally, PEG-DA and Gd3+ solutions are injected into the channels and cured by ultraviolet radiation