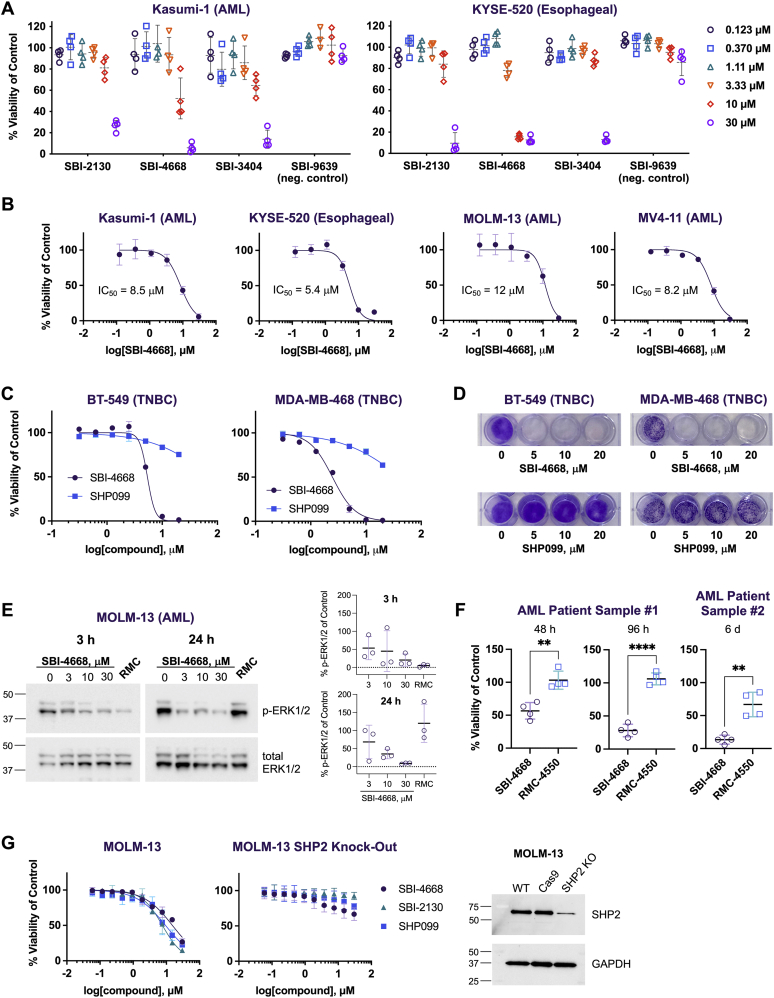
Figure 4.
Efficacy and selectivity of the SHP2 inhibitors in cellular cancer models and in patient-derived AML samples.A, viability of AML (Kasumi-1) and esophageal cancer (KYSE-520) cells in the presence of various concentrations of SHP2 active (SBI-2130, SBI-4668, and SBI-3404) and nonactive (SBI6339, negative control) furanylbenzamides after 3 days in culture. Cell viability is shown as a percentage of the vehicle (DMSO) control and represents the mean ± SD (n = 4). B, SBI-4668 dose–response curves in cell viability assays using Kasumi-1, KYSE-520, MOLM-13, and MV4-1 cells after 3 days in culture. The percentages compared with DMSO vehicle control were curve fitted using nonlinear regression (log[inhibitor] versus normalized response, variable slope) and represent the mean ± SD (n = 4). C, cell viability of BT-459 and MDA-MB-468 triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cells in the presence of various concentrations of SBI-4668 or the SHP2 allosteric inhibitor SHP099 after 5 days in culture. Cell viability is shown as a percentage of DMSO vehicle control, representing mean ± SD (n = 2), and curve fitted as in B. D, colony formation assay (11 days) of BT-459 and MDA-MB-468 TNBC cells in the presence of various concentrations of SBI-4668 or the SHP2 allosteric inhibitor SHP099. E, phospho-ERK1/2 (p-ERK1/2) immunoblot analysis from total cell lysates of MOLM-13 AML cells treated with SBI-4668 at the indicated concentrations or with SHP2 allosteric inhibitor RMC-4550 (RMC, 1 μM) for 3 h or 24 h. The quantitation of p-ERK1/2 levels is shown as the percentage of the DMSO (vehicle) control and represents data from three independent experiments (mean ± SD). F, viability of AML patient-derived cells in the presence of 10 μM SBI-4668 or 10 μM SHP2 allosteric inhibitor RMC-4550 after 2, 4, or 6 days in culture. Cell viability is shown as a percentage of the DMSO vehicle control and represents the mean ± SD (n = 4; ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001; unpaired t test with Welch's correction). G, viability of MOLM-13 cells and MOLM-13-Cas9-mCherry cells with SHP2 KO in the presence of SBI-2130, SBI-4668, and allosteric inhibitor SHP099 at various concentrations (10-point dose response). The percentages compared with the DMSO vehicle control were curve fitted using nonlinear regression (log[inhibitor] versus normalized response, variable slope) and represent the mean ± SD (n = 4). SHP2 protein levels in regular MOLM-13 cells (WT), MOLM-13-Cas9-mCherry cells (Cas9), and MOLM-13-Cas9-mCherry cells with SHP2 KO were evaluated by immunoblot analysis using SHP2 antibodies. AML, acute myeloid leukemia; DMSO, dimethyl sulfoxide; SHP2, Src-homology 2 domain–containing phosphatase 2.