Fig. 1.
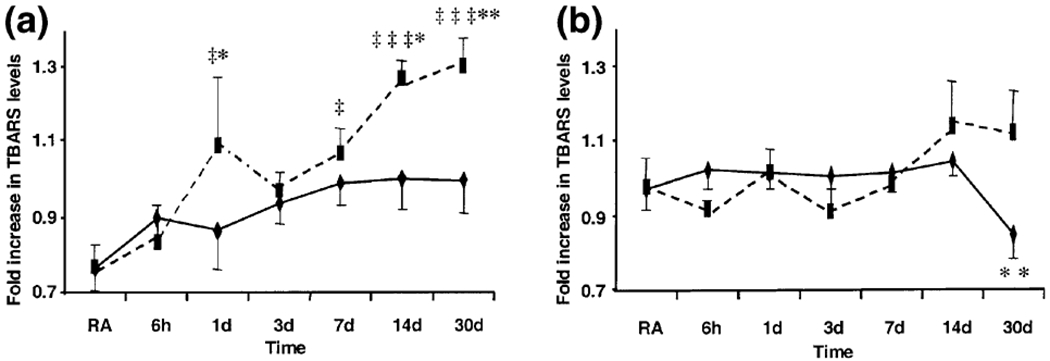
Thiobarbituric acid reactive substance (TBARS) levels in the (a) cerebellum and (b) pons of rats exposed to room air (RA, n = 6), chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH, diamonds, n = 6/time point) or chronic sustained hypoxia (CSH, squares, n = 6/time point). Bars represent standard error. (‡p < 0.05, ‡‡‡p < 0.001, CSH vs. RA; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 CSH vs. CIH, post-hoc Bonferroni.) Normalized RA values for cerebellum = 0.77 ± 0.06 and pons = 0.97 ± 0.06.
