FIGURE 5.
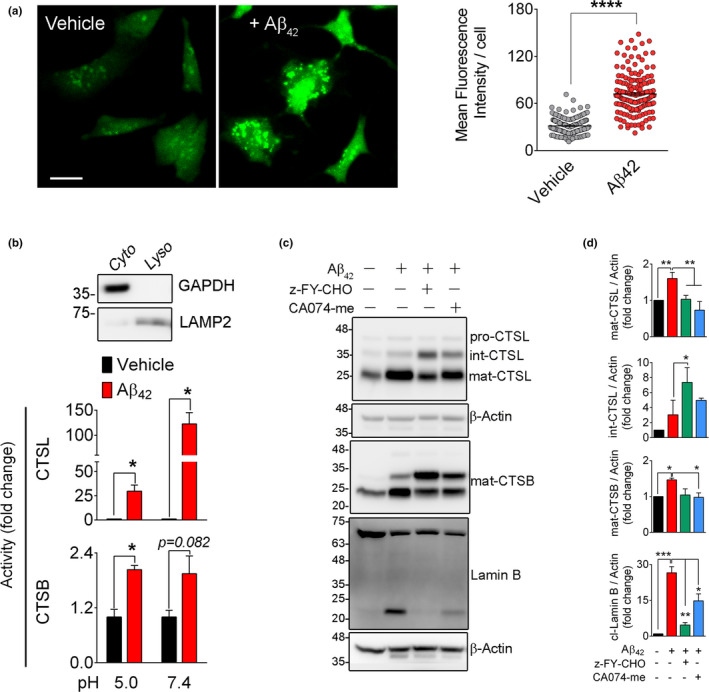
Lamin B1 damage in Aβ42 toxicity is associated with lysosomal membrane permeabilization. (a) Representative acridine orange staining confirmed the induction of LMP in Aβ42‐treated SH‐SY5Y cells. Scale bar = 20 µm. LMP was quantified using green fluorescence intensity/cell. A minimum of 100 cells/condition were examined. ****p < 0.0001. (t test) (b) LMP was further assessed by measuring CTSL and CTSB enzymatic activities in cytosolic fractions at pH 5.0 and pH 7.4. Data shown here represents mean ±SEM of n = 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.05. The purity of cytosolic fraction was confirmed by a Western blot against β‐actin (cytosol) and LAMP2 (lysosome). (c) Pharmacological inhibition of CTSL prevents Aβ42‐induced lamin B1 cleavage. SH‐SY5Y cells were pre‐treated with indicated inhibitors (20 µM each) overnight. Medium was changed, and cells were exposed to Aβ42 (5 µM) for 16 h. Cathepsin and lamin B were assessed by Western blotting in whole‐cell lysates. (d) Quantification of Western blot results in c, data presented as mean ± SEM, n = 3 independent experiments, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, and ***p < 0.001, respectively (one‐way ANOVA/Tukey's post hoc). Upregulation of cathepsin B and L coincided with appearance of the 21 kDa lamin B1 product in Aβ42‐treated group. This was robustly prevented by z‐FY‐CHO and partially by CA074‐me
