Figure 2. Exogenous Vasa mRNA is not retained selectively anywhere in the embryo.
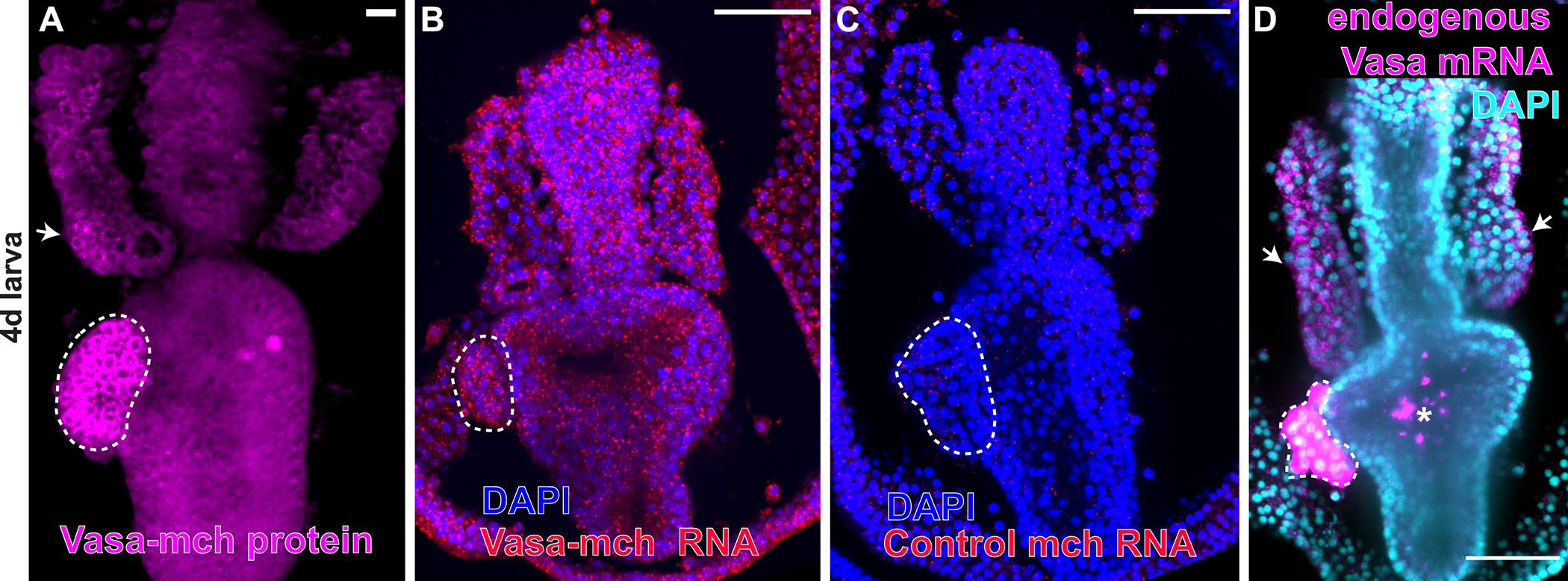
A) Exogenous Vasa-mCherry protein is enriched in the PE and in some cells of the anterior pouches (AP), white arrow. B) Fluorescent in situ hybridization of larvae expressing Vasa-mch using the mCherry probe detects Vasa-mCherry mRNA in every cell of the larva. C) A probe for mcherry used as a negative control shows no endogenous mcherry gene activity in wild type larvae. D) Detection of endogenous vasa mRNA in wild type larvae using a vasa antisense probe showing that vasa transcripts are expressed in the PE and in some cells of the AP (white arrows). Asterisk indicates non-specific fluorescence in the stomach of fed larvae. Scale bars = 50 μm. Dotted white lines highlight the PE. All figures show larvae 90–96h old.
