Figure 3. Gustavus is required for clearing Vasa protein in somatic tissues.
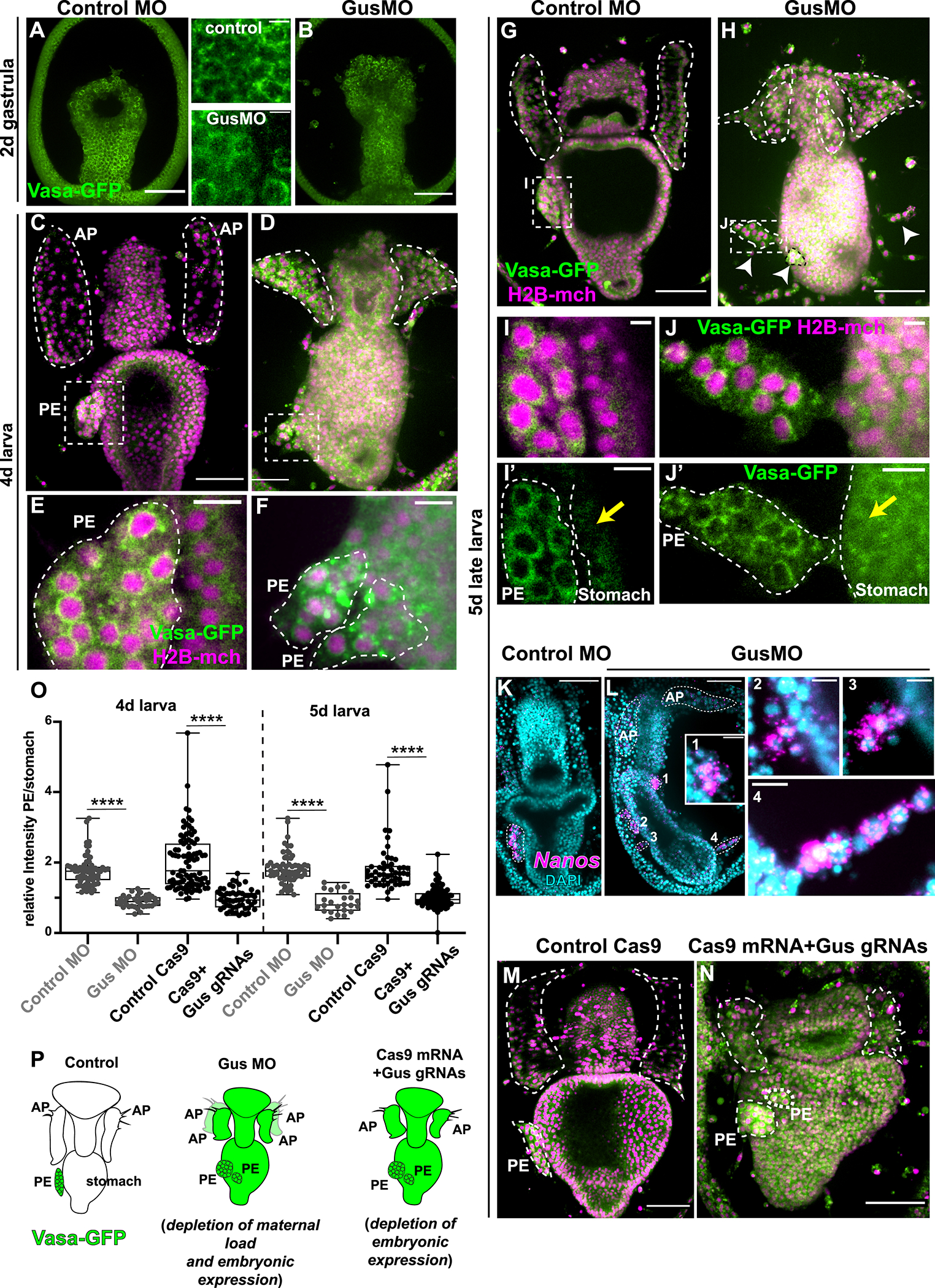
A,B) In gastrulae, Vasa-GFP protein is enriched perinuclearly in every cell-type in both controls and Gus morphants (see also inserts). C,D, E, F) 4 day larvae showing that in Gus morphants Vasa protein accumulates also in extra-PE tissues and the PE is fragmented G, H). At 5 days, controls have one PE on the left side of the stomach while Gus morphants have fragmented PEs (white arrowheads). I, J) In both controls and Gus-morphants, Vasa protein is localized perinuclearly in cells of the PE. Note that Vasa protein has accumulated in cells of the stomach of the Gus morphants only (yellow arrows). (For the GusMO phenotype at 5 days see also video 1 and 2. K, L) Fluorescent in situ hybridization showing that nanos transcripts are enriched in the PE in controls (K) and in the fragmented PEs in Gus morphants (L). Panels 1, 2, 3 and 4 are magnifications of the fragmented PEs from L that are enriched in nanos transcripts. AP and PEs are highlighted by white dotted lines. M) Controls (injected with Cas9 mRNA) and N) Gus knockout larvae (injected with Cas9 mRNA and 3 sgRNAs targeting Gus DNA) showing that preventing embryonic Gus expression causes fragmented PEs, vasa protein accumulation in all larval tissues and impaired APs. O) Quantification of Vasa protein enrichment in the PE with respect to the stomach in control MO and GusMO and in Cas9 control and Cas9 mRNA+ Gus sgRNAs in 4 and 5 day larvae. The ratio is close to 1 if the Vasa signal intensity is similar in the PE and the stomach, while it is >1 if the Vasa signal is stronger in the PE respect to the stomach. Student’s t-test gives p value <0.001 (****). P) Cartoon summarizing the main results. Exogenous vasa protein is shown in green. Vasa protein is degraded in the somatic tissue by a Gustavus-mediated mechanism so that Vasa is enriched in the PE only. Lack of Gustavus (using both morpholino and CRISPR-Cas9 approaches) results in ectopic Vasa protein expression in all somatic tissues and in the fragmented PEs. Note that when Gus is maternally depleted by blocking the overall protein translation there are 4 anterior pouches, while specifically blocking embryonic Gus expression results in smaller, but not supernumerary pouches. PE=posterior enterocoele (presumptive PGCs); AP= anterior pouches. Scale bar is 50μm in A,B,C,D,G,H,K,L, M,N and 5μm in I and J and 10μm in E,F, I’, J’, L1,L2,L3,L4.
