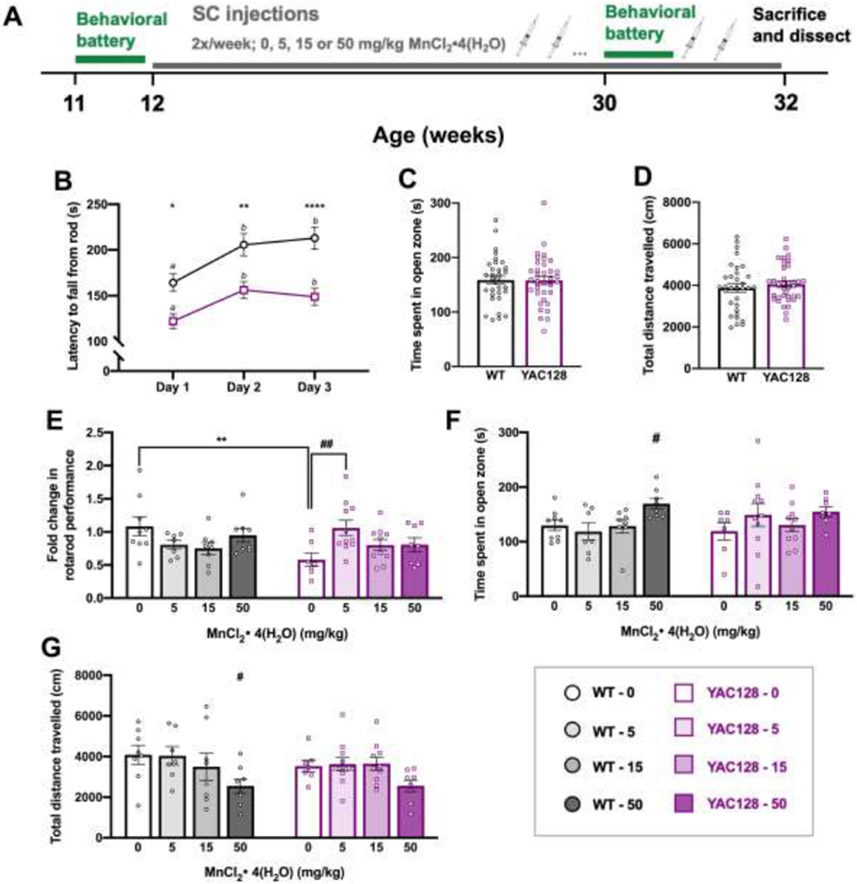
Figure 2.
Behavior chronic Study 1. (A) Experimental timeline for study 1 (n=68). Mice underwent a week-long baseline behavioral battery at 11 weeks old (B-D) prior to beginning twice weekly subcutaneous injections (0, 5, 15, or 50 mg/kg MnCl2 • 4(H2O)) from 12 weeks until 32 weeks of age. The behavioral battery was repeated at 30 weeks of age (E-G) to assess effects of chronic Mn exposure and mice were sacrificed and dissected at 32 weeks of age, 24 hours after the final injection. (B) Average latency to fall (3 trials per day; 300 s max per trial) from the rotarod across 3 days. Both genotypes display appropriate motor learning during the task, indicated by increased latency to fall on days 2 and 3 compared to day 1. YAC128 mice fall from the rod sooner than WT on all three days. Asterisks indicate a significant difference between genotypes on that day, and days that do not share a superscript letter are significantly different from each other within a genotype. (C) Anxiety-like behavior during a novel behavioral task was similar between genotypes at 11 weeks of age measured by time (s) spent in the open zone of the elevated zero maze (EZM). (D) Total distance travelled during 30 minutes in an open field chamber was comparable between WT and YAC128 mice. (E) Fold change in rotarod performance. Performance at 30 weeks for each individual mouse was divided by 11-week performance and plotted. Post-hoc follow-up tests showed that there was only a genotype difference in the vehicle dose (**), and within a genotype, the only significant Mn effect was between YAC128 vehicle and 5 mg/kg-exposed groups (##). (F) High dose Mn resulted in more time spent in the open zone of the EZM in WT mice. (G) WT mice receiving the highest dose of Mn were less active than vehicle-treated WT mice. For all, mean ± S.E.M. plotted unless otherwise noted. Asterisks * indicate genotype effect, pound # indicates Mn effect within genotype. # p <0.05, ## p <0.01, * p<0.05 **p<0.01, **** p<0.0001. n=7-11 per genotype-treatment group with approximately equal number of males and females.