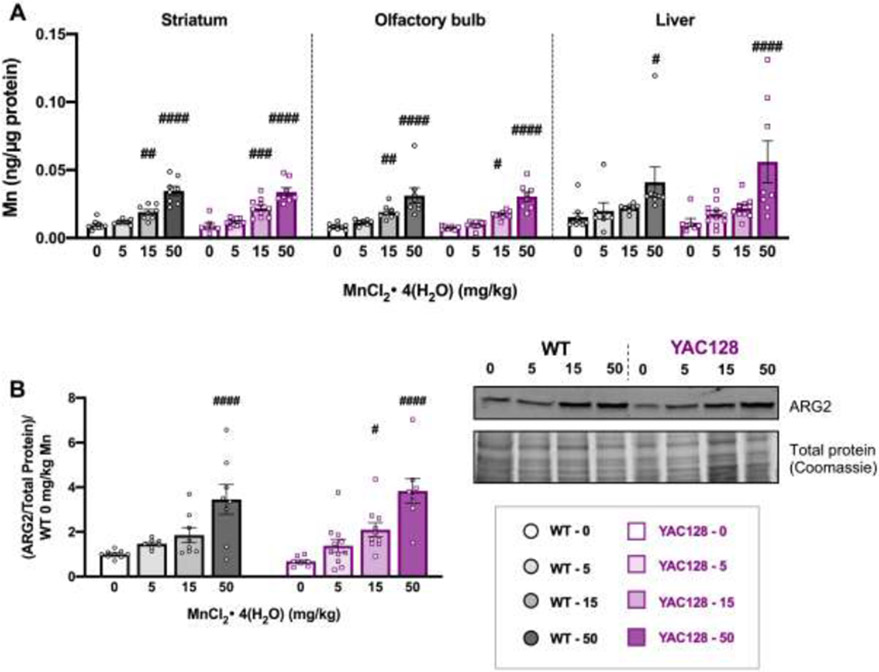
Figure 3.
Post-dissection outcomes for mice used in Study 1. (A) Mn levels (ng/μg protein) at 32 weeks of age for striatum (left), olfactory bulb (middle) and liver (right) from mice in Study 1 after 20 weeks of subcutaneous injections. Mn increased in all tissue types following exposure. Only 15 and 50 mg/kg significantly increased brain levels and only 50 mg/kg significantly increased hepatic Mn; # indicates significant differences from vehicle within each genotype by post-hoc Sidak’s multiple comparisons. (B) ARG2 protein expression normalized to total protein on gels by Coomassie blue staining for loading control and normalized to average WT 0 for each blot. Mn increased ARG2 expression in both genotypes, which were not different from each other. Within a genotype, only the 50 mg/kg dose was significantly higher than vehicle in WT and both 15 and 50 mg/kg doses led to a significant increase compared to its own genotype vehicle in YAC128, indicated by #. Representative blot and Coomassie stained gel are shown. For all, mean ± S.E.M. plotted unless otherwise noted. # p <0.05, ##, p<0.01, ### p<0.001, #### p<0.0001. n=7-11 per genotype-treatment group with approximately equal number of males and females.