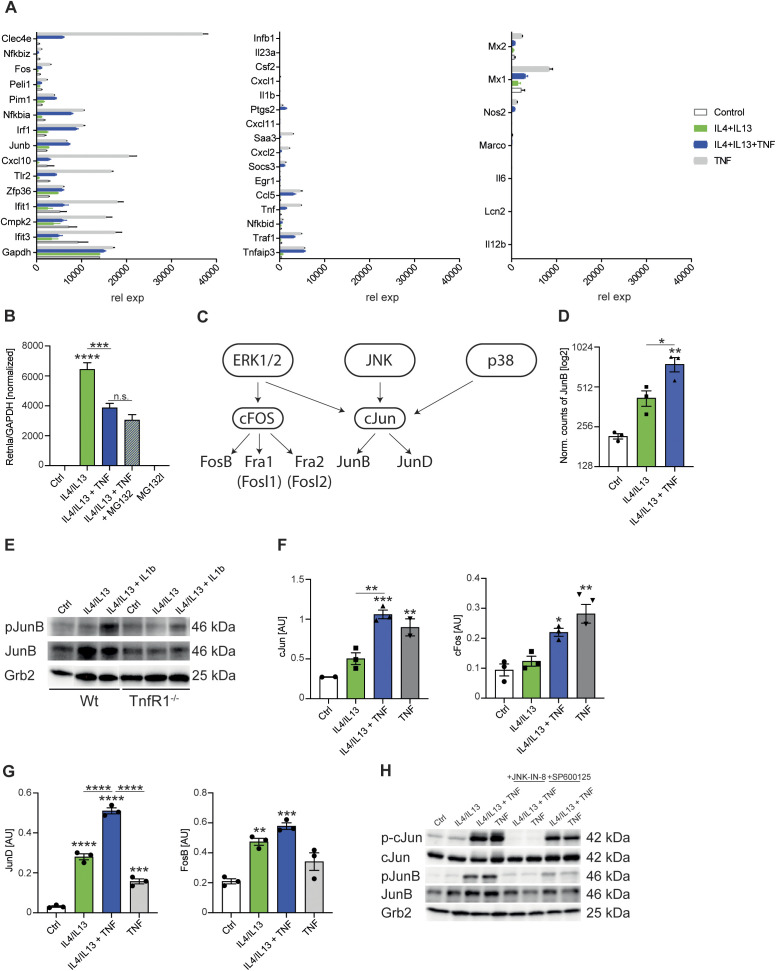
Figure S7. JNK signaling has broad and profound effects on macrophage polarization (related to Fig 6).
(A) Primary (left and middle) and secondary (right) NF-κB response genes of RNAseq profile. (B) Wild-type BMDMs were stimulated with IL4/IL13, IL4/IL13 + TNF or IL4/IL13 + TNF + MG132. TNF and MG132 was added 12 h after IL4/IL13 stimulation. The last time point was 18 h of IL4/IL13 stimulation. RNA was isolated and analyzed for Retnla expression. Data shown are the mean fold-increase of the Ctrl group. (C) Overview of the ERK/JNK/p38 pathway. (D) JunB gene analysis of transcriptomics data set from profile GSE169348. Graph shows IL4/IL13 or IL4/IL13 + TNF stimulated BMDMs after 6 h. (E) Wild-type and TnfR1−/− BMDMs were stimulated with IL4/IL13, IL4/IL13 + IL1β, or left untreated and whole-cell lysates were isolated and analyzed by Western blotting for the indicated proteins. All samples were blotted on one gel and sliced for the indicated groups. (F) AP-1 transcription factor assay kit was used to detect cJun and cFos after 15 min of stimulation. (G) JunD and FosB activation were analyzed with the AP-1 transcription factor assay kit. A spike-in experiment was used: 12 h after Il4/IL13 stimulation, TNF was added for further 150 min. (H) Wild-type BMDMs were pre-stimulated with JNK-IN-8 or SP600125 for 1 h before treatment with IL4/IL13, IL4/IL13 + TNF, or TNF (15 min) started. DMSO was added to the control groups. Whole-cell lysates were isolated and analyzed by Western blotting for the indicated proteins. All values are means ± SEM; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Statistically significant differences were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction. If not indicated otherwise, superscripts show statistical significance compared with the control group. n = 3 biological replicates.