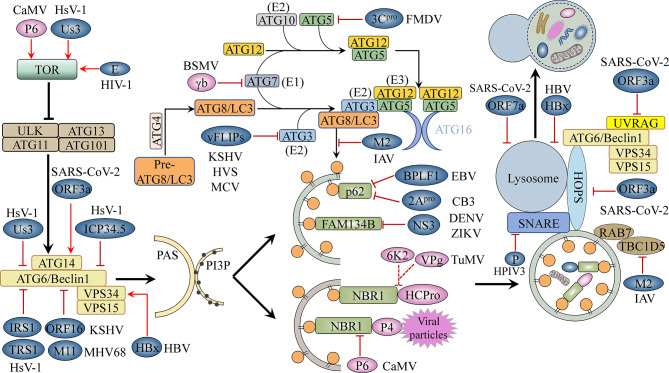
Figure 1.
The autophagy machinery and its inhibition by viruses. The ATG1/ULK1 complex, the ATG6/Beclin1-PI3K/VPS34 complex, and the ATG12-ATG5-ATG16 and ATG8-PE conjugation systems, among others, are involved in key steps of the autophagy pathway, including initiation, elongation, completion, and fusion. Viral proteins block cellular autophagy and promote virus development by activating TOR, a conserved Ser/Thr kinase; interacting with autophagy-related proteins, thereby inhibiting or promoting their activity; targeting selective autophagy processes; and interfering with autophagosome–lysosome fusion or lysosomal acidification. Blue-grey ovals represent animal viral proteins. Plant viral proteins are shown in pink. TOR, target of rapamycin; PAS, pre-autophagosomal structure; PI3P, phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate; E1/2/3, E1/2/3-like enzyme.