Figure 1.
Characterization of I37R-CFTR residual function in rectal biopsies and intestinal organoids
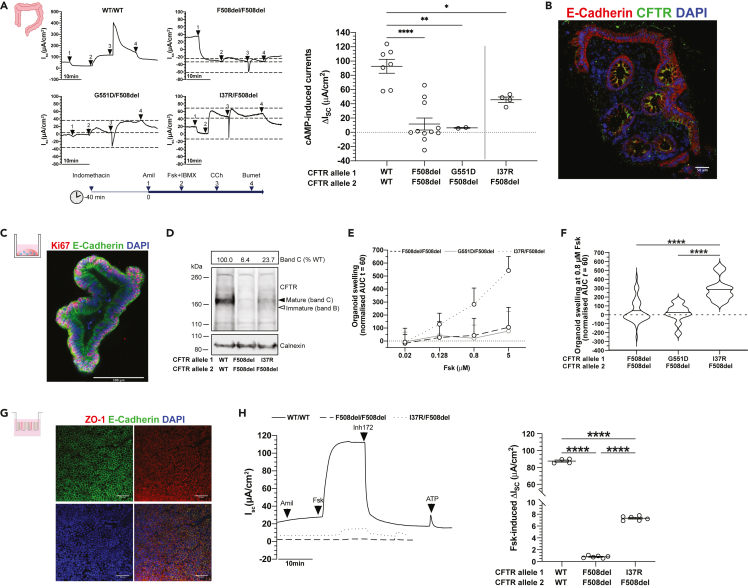
(A) Representative Ussing chamber recordings of intestinal current measurements (ICM) in rectal biopsies from WT-CFTR control participants and participants with CF. Dot plots of cAMP-induced current (ΔIsc-Fsk + IBMX) in participants with WT/WT (n = 2), F508del/F508del (n = 3), G551D/F508del (n = 1), and I37R/F508del (n = 1) CFTR genotypes. Experiments were performed in the presence of 10 μM indomethacin. Arrows indicate the addition of compounds: 100 μM apical amiloride (1. Amil), apical and basal addition of 10 μM forskolin +100 μM IBMX cocktail (2.Fsk + IBMX), 100 μM basal carbachol (3.CCh), and 100 μM basal bumetanide (4.Bumet). The Isc at the time CCh was added (middle horizontal dotted line), and the maximum (top dotted lines) and minimum (bottom dotted lines) Isc induced are indicated. Each dot represents an individual replicate.
(B) Immunofluorescence staining of CFTR (green), e-cadherin (red), and DAPI (blue) in a rectal biopsy derived from an I37R/F508del participant. 63x/1.4 oil immersion objective. Scale bar = 50 μm.
(C) Immunofluorescence staining of e-cadherin (green), Ki67 (red), and DAPI (blue) in intestinal organoids derived from an I37R/F508del participant. 20x/0.75 dry objective. Scale bar = 100 μm.
(D)Western blot in WT/WT, F508del/F508del, and I37R/F508del intestinal organoids. CFTR maturation was calculated by measuring the level of mature mutant CFTR (Band C) as a percentage of mature CFTR from WT organoids (% normal CFTR). All data were normalized to the calnexin loading control. B and C represents the mature, complex-glycosylated CFTR. B and B represents the immature, core-glycosylated CFTR. See Figure S9 for uncropped Western blot images.
(E and F) Forskolin-induced swelling (FIS) assay in organoids from participants with F508del/F508del (n = 5), G551D/F508del (n = 2), and I37R/F508del (n = 1) CFTR genotypes. Organoids were stimulated with forskolin (fsk) concentrations ranging from 0.02 to 5 μM.(E) FIS expressed as the means ± standard deviation (SD) of the area under the curve (AUC) calculated from t = 0 (baseline) to t = 60.(F) FIS of organoids at 0.8μM fsk at baseline represent residual CFTR function. Data represented as violin plots with mean to show distribution.
(G) Immunofluorescence staining of e-cadherin (green), ZO-1 (red), and DAPI (blue) in organoid-derived monolayers from a CF participant. 20x/0.75 dry objective. Scale bars = 50 μm.
(H) Representative Ussing chamber recordings of short circuit current in organoid-derived monolayers from a WT-CFTR control participant and participants with CF. Dot plots of fsk-induced current (ΔIsc-Fsk) in participants with WT/WT (n = 1), F508del/F508del (n = 1), and I37R/F508del (n = 1) CFTR genotypes. Experiments were performed in the presence of 10 μM indomethacin. Arrows indicate the addition of compounds: 100 μM apical amiloride, 5 μM basal fsk, 30 μM apical CFTR inhibitor CFTRinh-172, and 100 μM apical ATP. Each dot represents an individual replicate. Data in (A) and (H) represented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to determine statistical differences. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.