Figure 5.
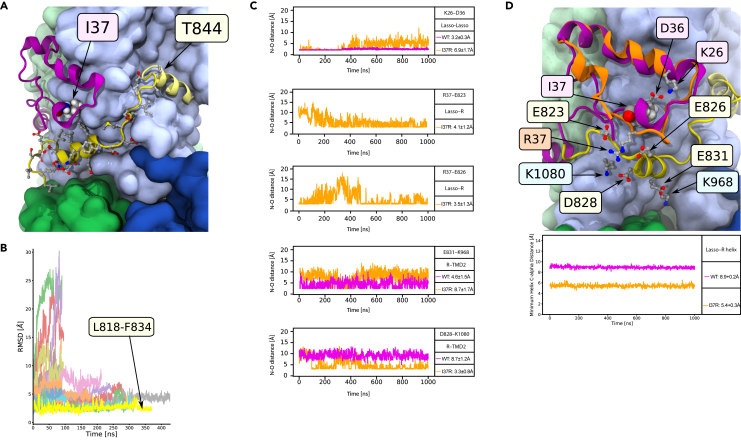
I37R interacts with a previously unresolved section of the R domain
(A) The reconstructed R domain amino acids (yellow), depicting the assignment of L818-F834 to the 17 amino acids with only the backbone resolved in the 6MSM structure, and the linking residues to T845 in TMD2. Lasso motif in purple. Side chains depicted as balls and sticks.
(B) The stabilities of all 24 modeled R domain assignments, quantified by RMSD to the 6MSM structure. The most stable alignment of the 17 unidentified amino acids, L818-F834, is highlighted yellow. The full list of tested assignments is shown in Supplementary material 9.
(C) The minimum N-O distance between newly formed and disrupted salt bridges in the I37R mutant. Distance less than 4 Å indicates direct contact. Values are means ± standard deviations (SD), sampled over the last 500 ns of simulations.
(D) Conformational changes in the I37R mutant (orange) compared to WT (purple) lasso motif, which brings it closer to the R domain (yellow). Minimum C-alpha atom distance between amino acid 37 and the R domain helix (E826-F834) in I37R and WT.