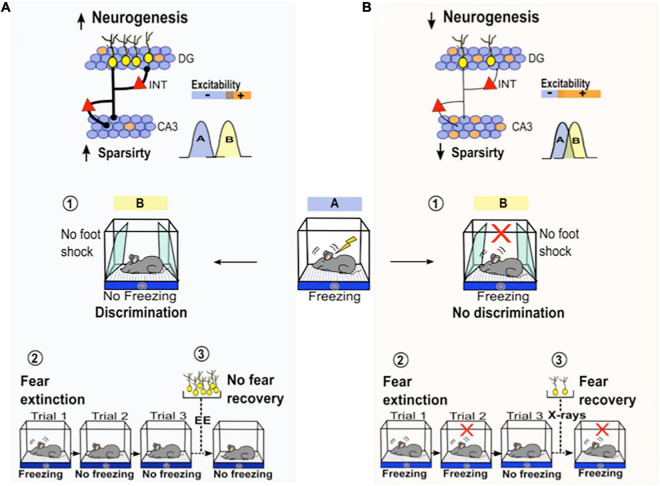
FIGURE 2.
The roles of adult neurogenesis in different contextual fear-related behaviors. (A) Activation of adult born- neurons (yellow neurons) activates GABAergic inhibitory interneurons (red triangles) in the DG and CA3 (Restivo et al., 2015; Temprana et al., 2015), which may increase sparsity activity in the DG-CA3 circuit potentially promoting pattern separation. Left below, the function of pattern separation prevents interference among different neuron population codes that are active during two similar experiences: A (blue) vs. B (yellow). This process facilitates the ability of the animal to discriminate between the conditioned context (A, blue) and a similarly close safe context (sloping walls, B yellow, ➀). Through this mechanism, AHN may promote fear memory extinction by reducing the interference between an old aversive memory association (context with foot shock) and a new safe association (context with no foot shock, ➁). After fear memory extinction, the increase in AHN by environmental enrichment (EE) prevents spontaneous fear recovery ➂. (B) A decrease in adult born- neurons reduces sparsity activity in the DG-CA3 circuit which may impair pattern separation (Niibori et al., 2012; Denny et al., 2014). Bottom right, low neurogenesis impairs pattern separation, which decreases the ability of an animal to discriminate between closely similar contexts ➀. Impairment in pattern separation due to low neurogenesis may also impair fear memory extinction. Rodents with low neurogenesis are not able to reduce the conditioned fear response (freezing) as efficiently as mice with normal levels of neurogenesis (trial 2 vs. trial 3) during extinction training ➁. The reduction in AHN by irradiation (X-ray) promotes spontaneous fear recovery ➂.