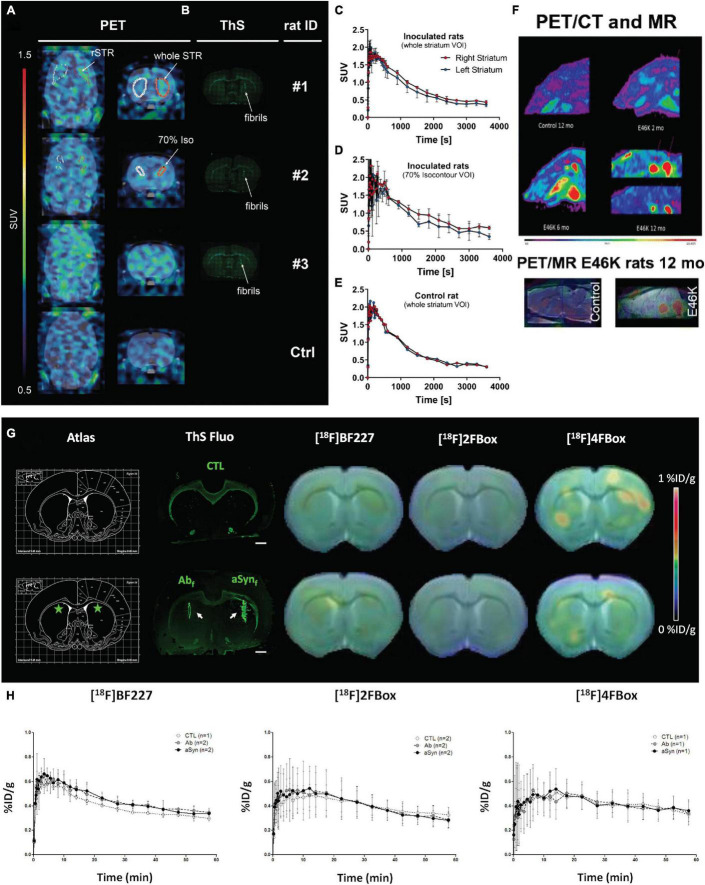
FIGURE 2.
In vivo α-synuclein imaging in animal models. (A–E) In vivo binding of (d3)-[11C]MODAG-001 in α-synuclein-inoculated rats. Coronal and transversal PET images (2.5–60 min) (A). Images show increased tracer accumulation in the α-synuclein fibril-inoculated right striatum compared with the vehicle-injected contralateral striatum. Thioflavin-S staining (B) indicated α-synuclein fibrils in the right striatum of fibril-inoculated rats (B). (C–E) Time activity curves of (d3)-[11C]MODAG-001 higher signal in the right (α-synuclein injected) than left (vehicle injected) striatum; α-SYN, α-synuclein; rSTR, right striatum; ThS, thioflavin S; Ctrl, control; SUV, standardized uptake value, DVR-1, distribution volume ratio-1; VOI, voxel of interest; Reproduced from Kuebler et al. (2021) with permission from Springer Nature. (F) [18F]DABTA-11 PET images in E46K rats show accumulation of the tracer in the medulla oblongata. The accumulation is apparent even at 2 months of age and is more prominent at 6 and 12 months of age with detectable uptake in the substantia nigra. PET/MRI and rat brain atlas confirm the regional uptake of the tracer. Reproduced from Yousefi et al. (2016) and Aboagye and Kraeber-Bodéré (2017) with permission from Springer Nature. (G,H) small-animal PET imaging with [18F]BF227, [18F]2FBox, and [18F]4FBox in control and fibril-injected rats. (G) Summed PET images were coregistered with CT images, and the radioactivity index was reflected by a color scale representing %ID/g. ThS fluorescence staining of Aβ42 and α-syn fibrils injected in the striata is presented (white arrows), with the corresponding stereotaxic brain atlas region (green stars representing injection sites). Scale bar represents 1 mm on ThS fluorescence staining. (H) Time activity curves (expressed in %ID/g over time) for each radiotracer are presented. Values (mean ± SD) were extracted from the striata regions based on an in-house-made MRI atlas that was coregistered to PET-CT images. Reproduced from Verdurand et al. (2018) with permission from American Chemical Society.