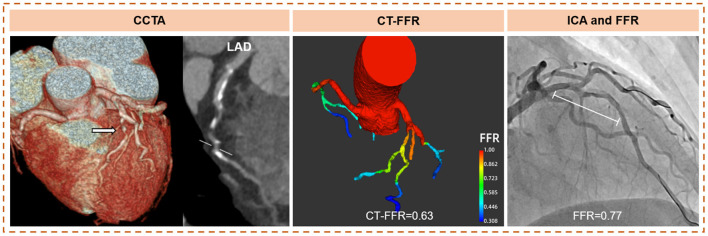
Figure 5.
Case of CT-FFR estimating coronary lesions with severe calcification. Example of a 66-year-old female with stable chest pain. The CAC scores of LAD, LCX, and RCA were 599.6, 216.4, and 716.2. CCTA showed multiple calcified and mixed plaques causing more than 70% stenosis in the proximal and mid LAD. CT-FFR demonstrated functional ischemia (CT-FFR = 0.63) caused by LAD stenosis, and confirmed by FFR (FFR = 0.77). The deviation of CT-FFR was 0.14 in the situation of severe coronary calcification. With the widely-accepted threshold of ischemia ( ≤ 0.8), CT-FFR made a correct dichotomous diagnosis. LAD, left anterior descending coronary artery; LCX, left circumflex artery; RCA, right coronary artery; CT-FFR, computed tomography derived fractional flow reserve; FFR, fractional flow reserve; CAC, coronary artery calcium; CTA, computed tomography angiography.