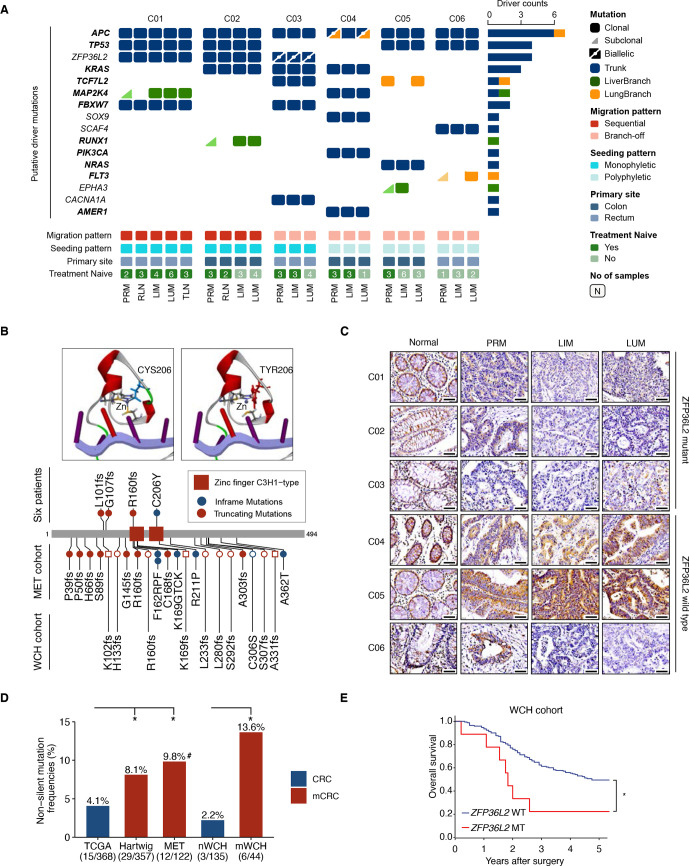
Figure 5.
Identification of ZFP36L2 as a candidate driver gene in metastatic CRC. (A) An overview of somatic putative driver mutations detected in matched primary and metastatic tumours across six patients. The mutation events of each gene across all patients are shown. Genes in the COSMIC cancer gene census are bolded. Trunk, LiverBranch and LungBranch mutations were colour-labelled as blue, green, and orange respectively. Biallelic mutations are shown as triangles with a dot-labelled split line. (B) The wide-type and C206Y mutated zinc finger domain structure of ZFP36L2. C206Y mutated ZFP36L2 lost the interaction with zinc atom (top). Detailed information of ZFP36L2 mutations in different cohorts. circle and square indicate patients in mWCH and nWCH, respectively (bottom). (C) Immunohistochemical staining of ZFP36L2 in matched primary and metastatic tumours across six patients; scale bar, 50 µm. (D) Non-silent mutation frequencies of ZFP36L2 in five cohorts of microsatellite stable CRC: TCGA, primary tumour samples from COAD/READ in TCGA; Hartwig cohort, metastatic colorectal cancer samples from Hartwig cancer cohort; MET cohort, distant metastatic samples; nWCH, primary tumour samples from patients with no distant metastasis; mWCH, primary tumour samples from patients with distant metastasis; (*p<0.05; χ2 test; #mutated in both primary tumours and liver metastasis); (E) Kaplan-Meier estimates of overall survival in the WCH cohort stratified by the ZFP36L2 mutation status (*p<0.05, log-rank test). CRC, colorectal cancer; LIM, liver metastasis; LUM, lung metastasis; PRM, primary tumour; TCGA, The Cancer Genome Atlas.