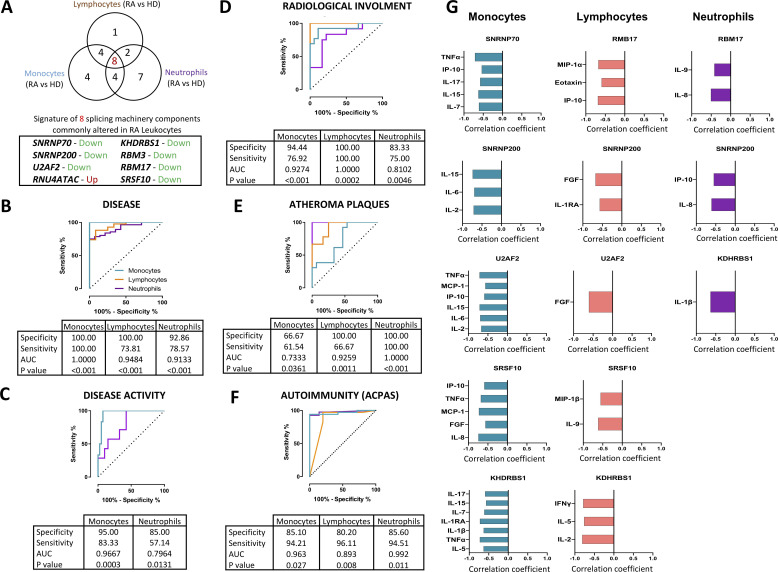
Figure 2.
A signature of eight components of the splicing machinery is commonly altered in RA leucocytes and associated with clinical features of RA. (A) Venn diagram of differentially expressed splicing machinery elements in RA versus HD in leucocyte subtypes (monocytes, lymphocytes and neutrophils). A signature of eight spliceosome components commonly altered in all cell types are also highlighted indicating the direction of that alteration. The potential of this signature in each cell type as biomarkers of disease (B), disease activity (C), radiological involvement (D), atheroma plaques (E) and ACPAs positivity (F) were further demonstrated through logistic regression and receiver operating characteristic curve analysis. Area under the curve (AUC), specificity, sensitivity and p value are displayed in each analysis. (G) Correlation analysis between the signature of eight spliceosome components in each leucocyte subtype and the plasma pro-inflammatory profile was performed, and those showing a p<0.05 are shown. Spearman correlation coefficient is displayed where appropriate. ACPAs, anti-citrullinated protein antibodies; FG, fibroblast growth factor; HD, healthy donors; IFN, interferon; IL, interleukin; IP, interferon gamma-induced protein; MCP, monocyte chemoattractant protein; RA, rheumatoid arthritis; TNF, tumour necrosis factor.