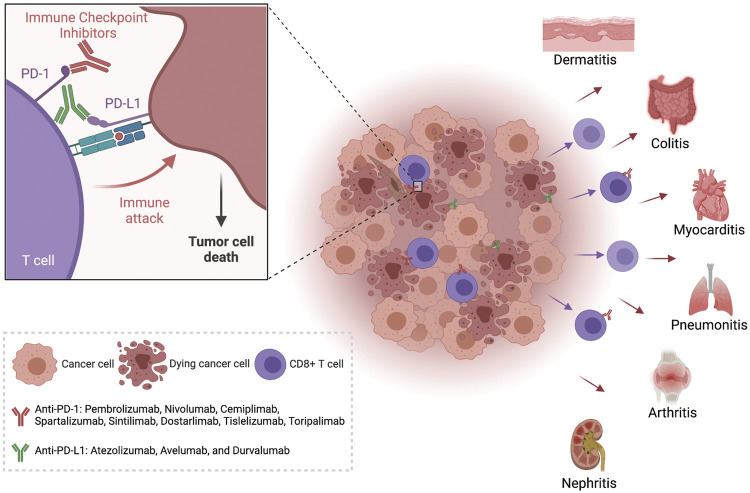
FIGURE 1.
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors can lead to the development of inflammation in many organs. The treatment of tumors with anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L 1 antibodies increases the activation of tumor infiltrating cytotoxic T cells and leads to tumor cell death. These activated T cells with decreased function of the PD-1 checkpoint pathway have also been observed in peripheral circulation and have been isolated from inflamed organs in patients with immune related adverse events (irAEs). Created with Biorender.com.