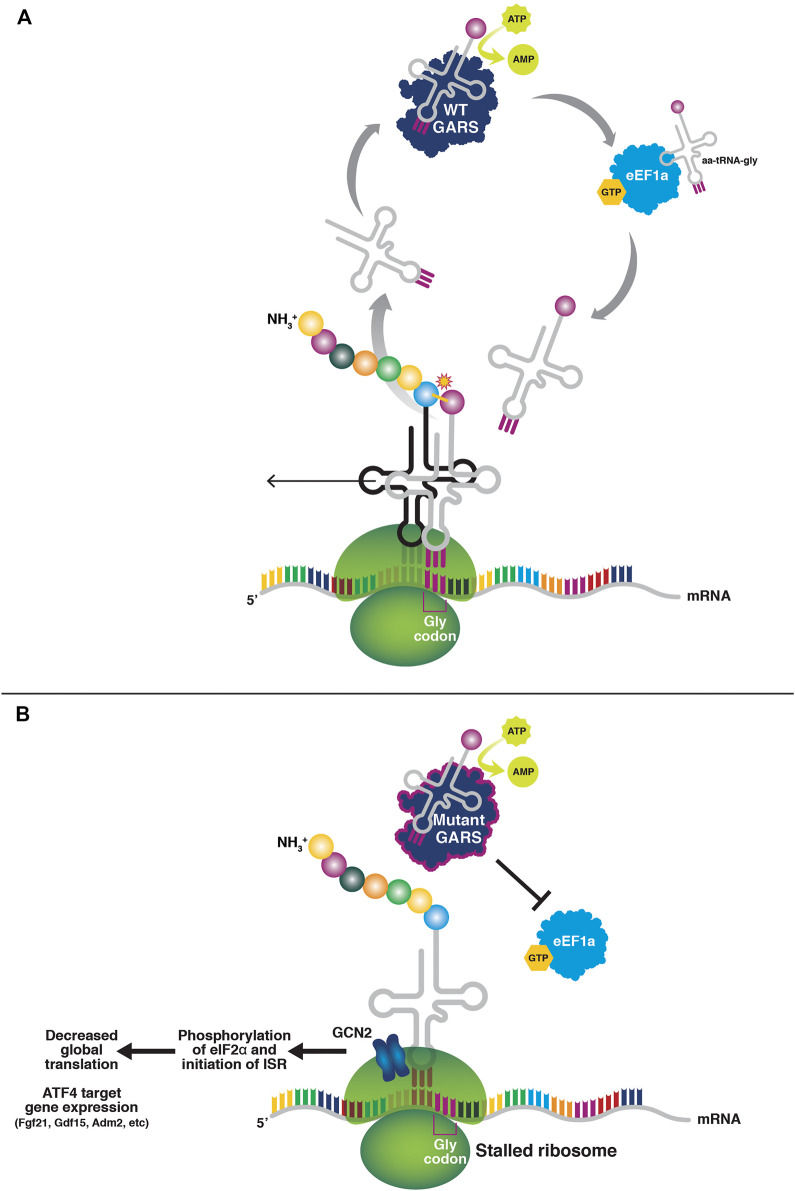
FIGURE 1.
tRNA sequestration by mutant tRNA synthetases. (A) In normal tRNA charging, the amino acid binds the tRNA synthetase and is coupled with ATP to form an aminoadenylate intermediate. The amino acid is then charged onto the 3′ end of the cognate tRNA. The amino acid-charged tRNA is shuttled to the ribosome by eEF1A to participate in translation. (B) Mutant tRNA synthetases do not release the tRNAs to eEF1A, thus resulting in a paucity of charged tRNAs for translation elongation and subsequently ribosome stalling at Glycine codons (in the case of mutant glycyl tRNA-synthetase). The stalled ribosomes activate GCN2 and the integrated stress response, resulting in a suppression of global cap-dependent translation through eIF2α phosphorylation, and activation of ATF4 target gene expression.