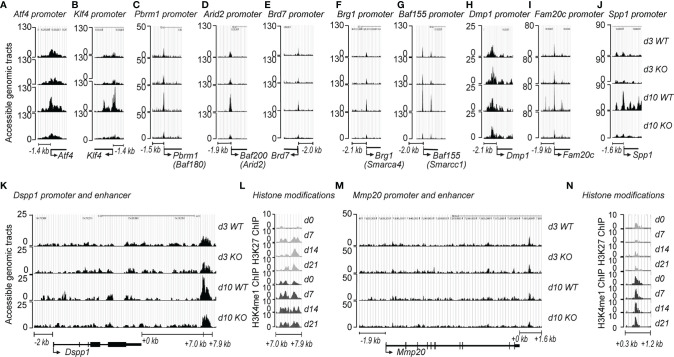
Figure 5.
BAF45A-PBAF complex regulates chromatin accessibility and bone-specific gene transcriptional network. Baf45a floxed allele was deleted in primary calvarial osteoblasts via 4-hydroxytamoxifen inducible CAG-Cre genetic background. The cells were then subjected to osteogenic differentiation. Osteoblasts were harvested at day 3 and day 10 of differentiation. ATAC-seq was performed on WT and Baf45a knockout osteoblasts. (A, B) Chromatin accessibility at the gene loci of transcriptional factors Atf4 and Klf4, (C–G) Genomic accessibility profiles of PBAF subunits, and tooth and bone-related genes (H) Dmp1, (I) Fam20c, (J) Spp1, (K) Dspp1, and Mmp20 (M). ChIP-sequencing analysis was performed in BMSCs using the anti-H3K27ac and anti-H3K4me1 antibodies to identify downstream enhancer regions of bone and tooth-related genes (L) Dspp1, (N) Mmp20. “Y-axis” indicates accessible genomic tracts, and the “X” axis denotes the genomic regions.