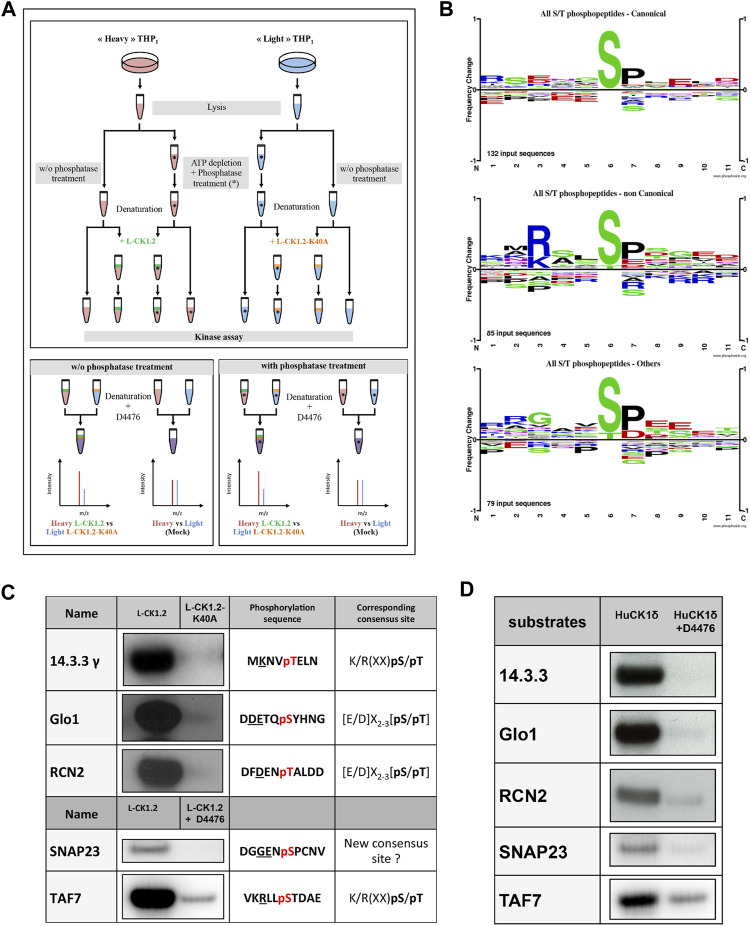
FIGURE 1.
Experimental workflow and validation of substrate dataset. (A) Upper Panel. Workflow diagram showing the experimental strategy used to reveal L-CK1.2 substratome derived from THP-1 lysates. THP1 cells were cultured and differentiated in the presence of natural amino acids (light, blue) or stable amino acid isotopes (heavy, red). Equal amounts per reaction (0.5 mg) of heavy or light lysates were treated with phosphatase and ATP depleted (*) or not and denatured by heat inactivation to remove endogenous kinase activities. The phosphatase reactions were stopped by heat inactivation. Lysates were then subjected to IVKA in presence of recombinant L-CK1.2 (green), L-CK1.2-K40A (kinase-dead, orange), or were mock treated with equal amounts of kinase elution buffer, in triplicate. The reactions were stopped with heat inactivation and addition of 10 μM D4476. Lower panel. Equal amounts (0.5 mg) of heavy (L-CK1.2) and light (L-CK1.2-K40A) samples were mixed. In addition, mock heavy and light samples were mixed in a 1:1 ratio and used as a control. The four samples were reduced, alkylated and digested and the resulting phospho-peptides were enriched by TiO2-affinity chromatography, and processed by LC-MS/MS analysis on an Orbitrap fusion mass spectrometer. (B) Sequence logos analysis of unique phospho-sites (five amino acids before and after the phosphorylation residues) matching strict selection criteria. Upper panel, for canonical consensus sites; middle panel, for non-canonical sites; and lower panel, for others. The amino acids are labelled according to their chemical properties: green for polar amino acids (G, S, T, Y, C, Q, N), blue for basic amino acids (K, R, H), red for acidic amino acids (D, E), and black for hydrophobic amino acids (A, V, L, I, P, W, F, M). (C) Autoradiogram representing IVKA using selected recombinant human proteins and inactive L-CK1.2-K40A (kinase-dead), active L-CK1.2 alone or in presence of the CK1-specific small molecule inhibitor D4476 (10 μM). (D) Autoradiogram representing IVKA using selected recombinant human proteins and recombinant CK1δTV1 alone or in the presence of D4476.