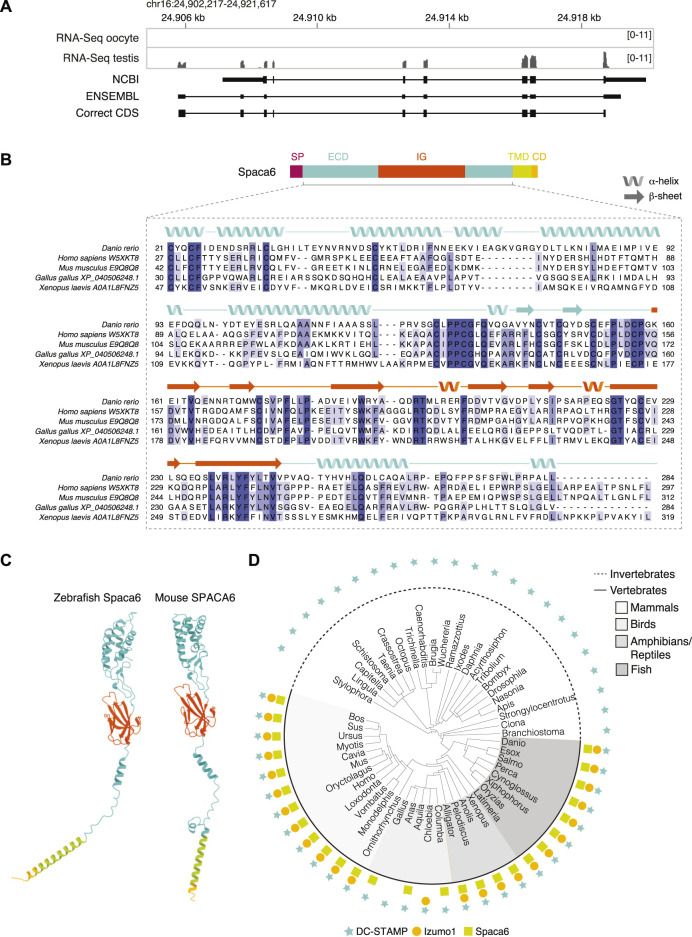
FIGURE 1.
Identification of Spaca6 in zebrafish. (A). Expression and genomic features of zebrafish spaca6. Coverage tracks for RNA sequencing data from oocyte and testis aligned with ENSEMBL (ENSDART00000155083.2) and NCBI (XM_021466914.1) annotations as well as the full-length, newly identified testis coding DNA sequence (correct CDS). Genomic coordinates are based on GRCz11. (B). Protein domain structure of full-length Spaca6 and sequence alignment of the mature extracellular region of selected vertebrate Spaca6 proteins. Secondary structure prediction of the zebrafish Spaca6 protein sequence is depicted above the sequence alignment (coil: alpha-helix; arrow: beta-sheet). The extracellular domain (ECD) is shown in blue, while the Immunoglobulin-like domain (IG) is shown in orange. SP, signal peptide; TMD, Transmembrane domain; CD, Cytoplasmic domain. (C). Tertiary structure predictions of mouse and zebrafish Spaca6. Protein folding predictions of mature Spaca6 (lacking the signal peptide sequence) were performed using AlphaFold2 (Jumper et al., 2021). Extracellular domain, blue; Ig-like domain, orange; Transmembrane domain, green; Cytoplasmic domain, yellow. (D). Taxonomic tree of DC-STAMP-like proteins, Izumo1 and Spaca6 across vertebrates and invertebrates. DC-STAMP-like proteins (blue star) are conserved both in vertebrates and invertebrates; Izumo1 (orange circle) and Spaca6 (green square) are conserved only in vertebrates.