Fig. 1.
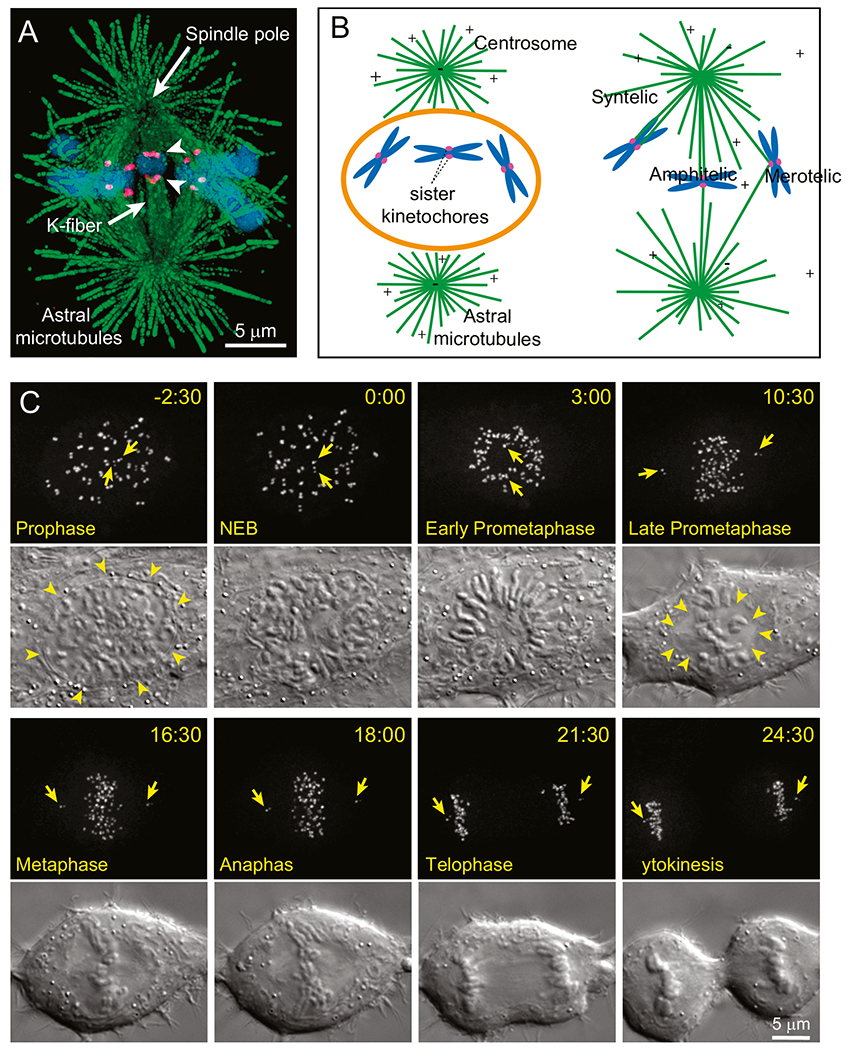
Mitotic machinery and the principle of spindle assembly (A) Architecture of mitotic spindle. Two radial arrays of microtubules (green) emanate from the spindle poles. Bundles of MTs (K-fibers) connect spindle poles and kinetochores (magenta), specialized organelles on chromosomes (blue). Arrowheads denote sister kinetochores on a chromosome that is simultaneously attached to the opposite spindle poles (i.e., ‘amphitelic’). The image depicts a medial slice through the metaphase spindle of Indian muntjac, a species of deer that possesses the largest kinetochores among mammals. (B) Cartoon of the ‘Search and Capture’ model for spindle assembly. Breakdown of the nuclear envelope (orange) at the onset of mitosis allows microtubules (green) that radially emanate from the centrosomes to reach chromosomes (blue). Connection to a spindle pole is achieved via capture of microtubules by the kinetochores (magenta). Due to stochasticity in the distribution of chromosomes and growth of microtubules, capture may lead to a proper amphitelic attachment as well as to erroneous configurations when a single kinetochore simultaneously attaches to both spindle poles (‘merotelic’ attachment) or when sister kinetochores attach to the same spindle pole (‘syntelic’ attachment). For faithful chromosome segregation, amphitelic attachments should be promoted while erroneous attachments – suppressed. (C) Progression through mitosis in a typical human cell. Kinetochores and centrosomes, labelled with CENP-A-GFP and centrin1-GFP respectively, are shown as Maximum Intensity Projections through the entire cell. Arrows denote pairs of centrioles within each centrosome/spindle pole. Changes in cell morphology are shown in Differential Interference Contrast (DIC). Spindle assembly initiates when nuclear envelope breaks down (NEB, arrowheads). Chromosomes arrange in a characteristic ring around the forming spindle during Early Prometaphase and later repopulate the centre of the inner parts of the spindle forming a tight plate at the equator by Metaphase. The spindle assembles within a clear zone devoid of large organelles (Late Prometaphase, arrowheads). Notice rounding of the cell as it progresses through spindle assembly. Chromosome segregation occurs rapidly during Anaphase that initiates less than 20 min after NEB and daughter cells form during Cytokinesis.
