Figure 1.
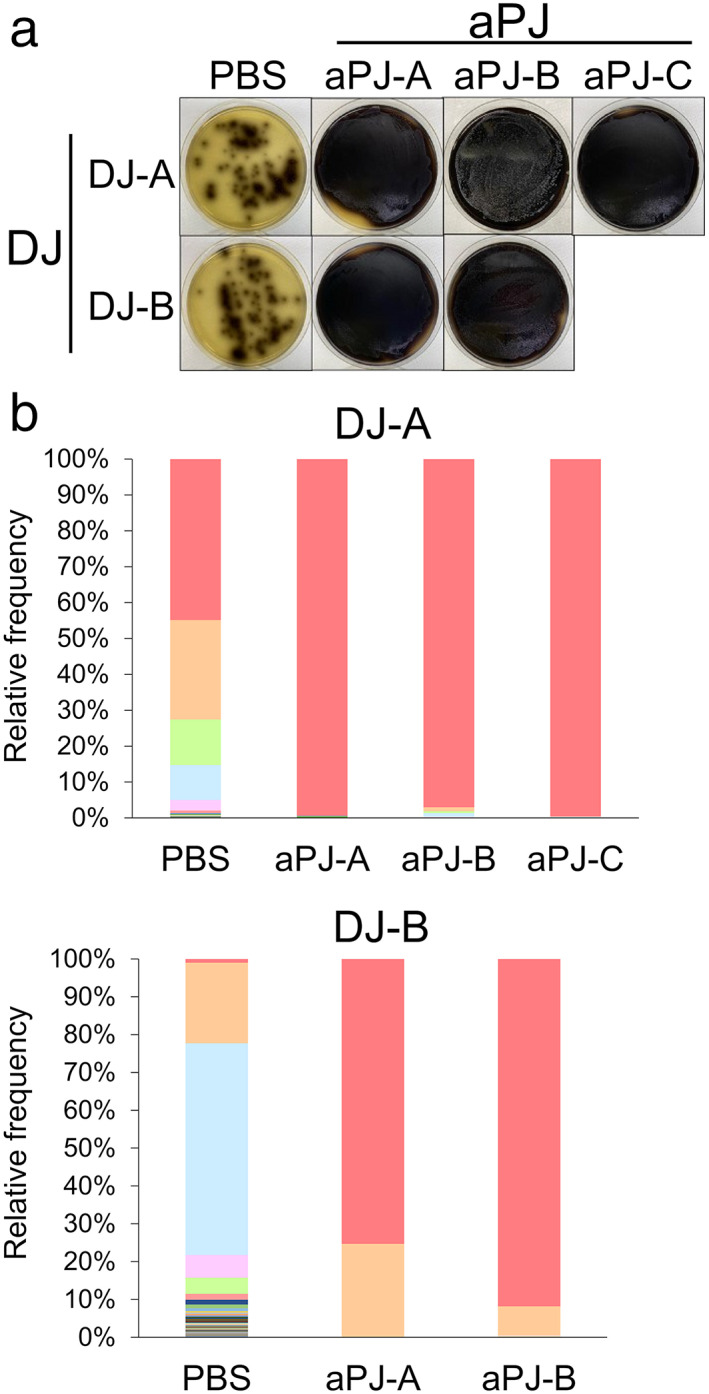
Enterococcus spp. have higher fitness to survive in pancreatic juice. (a) Visual agar plate assay to detect the abundance of Enterococcus spp. in a mixture of duodenal juice (DJ) and aseptic pancreatic juice (aPJ) at a 1:49 volume ratio. The DJ/aPJ mixture was incubated for 24 h before plating on Enterococcosel agar. Phosphate‐buffered saline was used as a control instead of aPJ. (b) Metagenome analysis of the DJ/aPJ mixture. After incubation, the samples were subjected to 16S rRNA metagenome analysis without selection on the agar plate. Each colored bar indicates the relative frequency of indicated bacterial species, which are listed on the right panel. ( ), Enterococcus spp.; (
), Enterococcus spp.; ( ), Enterobacteriaceae; (
), Enterobacteriaceae; ( ), Veillonella; (
), Veillonella; ( ), Bifidobacterium animalis; (
), Bifidobacterium animalis; ( ), Klebsiella; (
), Klebsiella; ( ), Enterococcus spp.; (
), Enterococcus spp.; ( ), Enterocuccus casseliflavus; (
), Enterocuccus casseliflavus; ( ), Bacteroides spp.; (
), Bacteroides spp.; ( ), Enterobacteriaceae; (
), Enterobacteriaceae; ( ), Fusobacterium spp. aPJ‐A, aseptic pancreatic juice from ampullary cancer; aPJ‐B, aseptic pancreatic juice from pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; aPJ‐C, aseptic pancreatic juice from duodenal cancer; PBS, phosphate‐buffered saline.
), Fusobacterium spp. aPJ‐A, aseptic pancreatic juice from ampullary cancer; aPJ‐B, aseptic pancreatic juice from pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor; aPJ‐C, aseptic pancreatic juice from duodenal cancer; PBS, phosphate‐buffered saline.
