Figure 4.
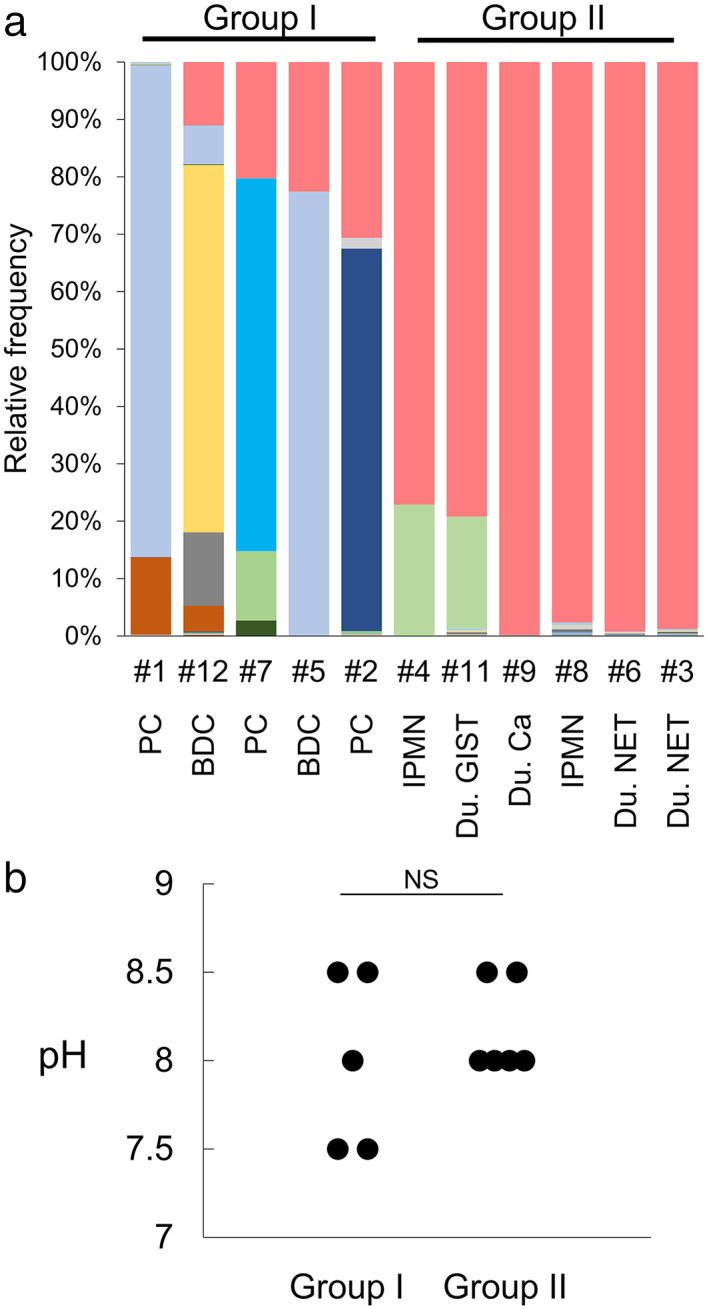
Microbiota in pancreatic juice is diverse in patients with pancreatobiliary cancer but is highly enriched with Enterococcus spp. in patients with duodenal region tumors and IPMN. (a) Metagenome analysis of 11 pancreatic juice samples. 16S rRNA metagenome analysis was performed on pancreatic juice samples from the indicated cases. Each colored bar indicates the relative frequency of the indicated bacterial species, which are listed on the right panel. ( ), Enterococcus spp.; (
), Enterococcus spp.; ( ), Enterobacteriaceae; (
), Enterobacteriaceae; ( ), Stenotrophomonas spp.; (
), Stenotrophomonas spp.; ( ), Stenotrophomonas spp.; (
), Stenotrophomonas spp.; ( ), Pseudomonas spp.; (
), Pseudomonas spp.; ( ), Aeromonas caviae; (
), Aeromonas caviae; ( ), Klebsiella oxytoca; (
), Klebsiella oxytoca; ( ), Escherichia coli; (
), Escherichia coli; ( ), Stenotrophomonas geniculata; (
), Stenotrophomonas geniculata; ( ), Enterococcaceae. (b) Comparison of pH levels in pancreatic juice samples of patients with pancreatobiliary cancer versus those with duodenal tumors and IPMN. Wilcoxon rank‐sum test was used for the statistical analysis. BDC, bile duct cancer; Du, duodenal‐; IPMN, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia; PC, pancreatic cancer.
), Enterococcaceae. (b) Comparison of pH levels in pancreatic juice samples of patients with pancreatobiliary cancer versus those with duodenal tumors and IPMN. Wilcoxon rank‐sum test was used for the statistical analysis. BDC, bile duct cancer; Du, duodenal‐; IPMN, intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasia; PC, pancreatic cancer.
