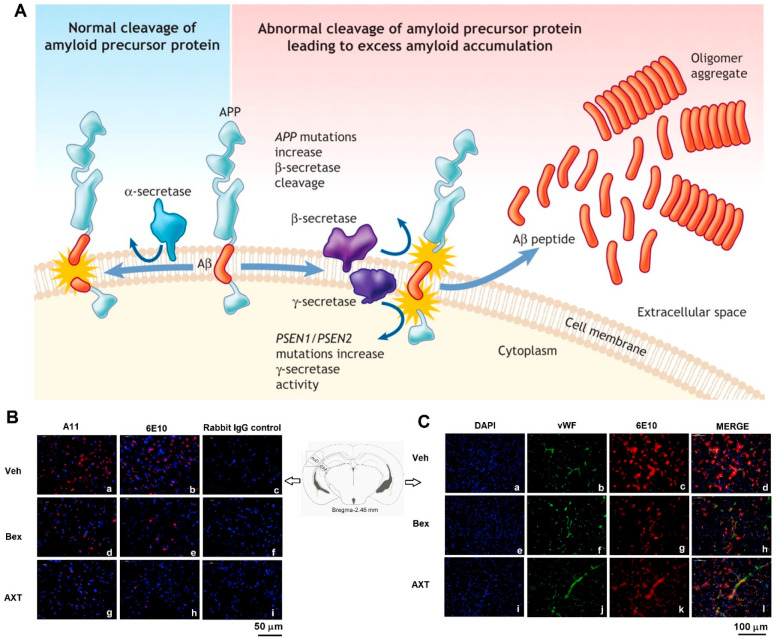
Figure 9.
(A) As a transmembrane protein, the amyloid precursor protein (APP) undergoes a series of proteolytic cleavages by secretase enzymes. It is not amyloidogenic if APP is cleaved through α-secretase in the middle of Aβ, but the cleavage through β- and γ-secretase enzymes is accompanied by the release of neurotoxic Aβ peptides which can accumulate into an oligomer aggregate. The APP gene mutations prevent the cleavage through α-secretase followed by enabling the preferential cleavage through β-secretase. Mutations in the presenilin-1 and presenilin-2 genes (PSEN1 and PSEN2), which are regarded as the components of the γ-secretase complex, raise the cleavage through γ-secretase at this site. Notably, both situations result in the production of excess Aβ peptide. Over time, the oxidative stress causes neuronal death followed by the development of neuritic plaques typical of Alzheimer’s disease. Reprinted from ref (158) with permission from CMAJ. (B) Immunofluorescence staining was conducted on 18 μm sections of the mouse brain. (C) Immunofluorescence double staining was conducted on 18 μm sections of the mouse brains. Vehicle (Veh), bexarotene (Bex), and astaxanthin (AXT). Reprinted from ref (141) with permission of Elsevier.