Fig. 1. CLP290 rescued PB-resistant neonatal seizures in P7 CD1 mice.
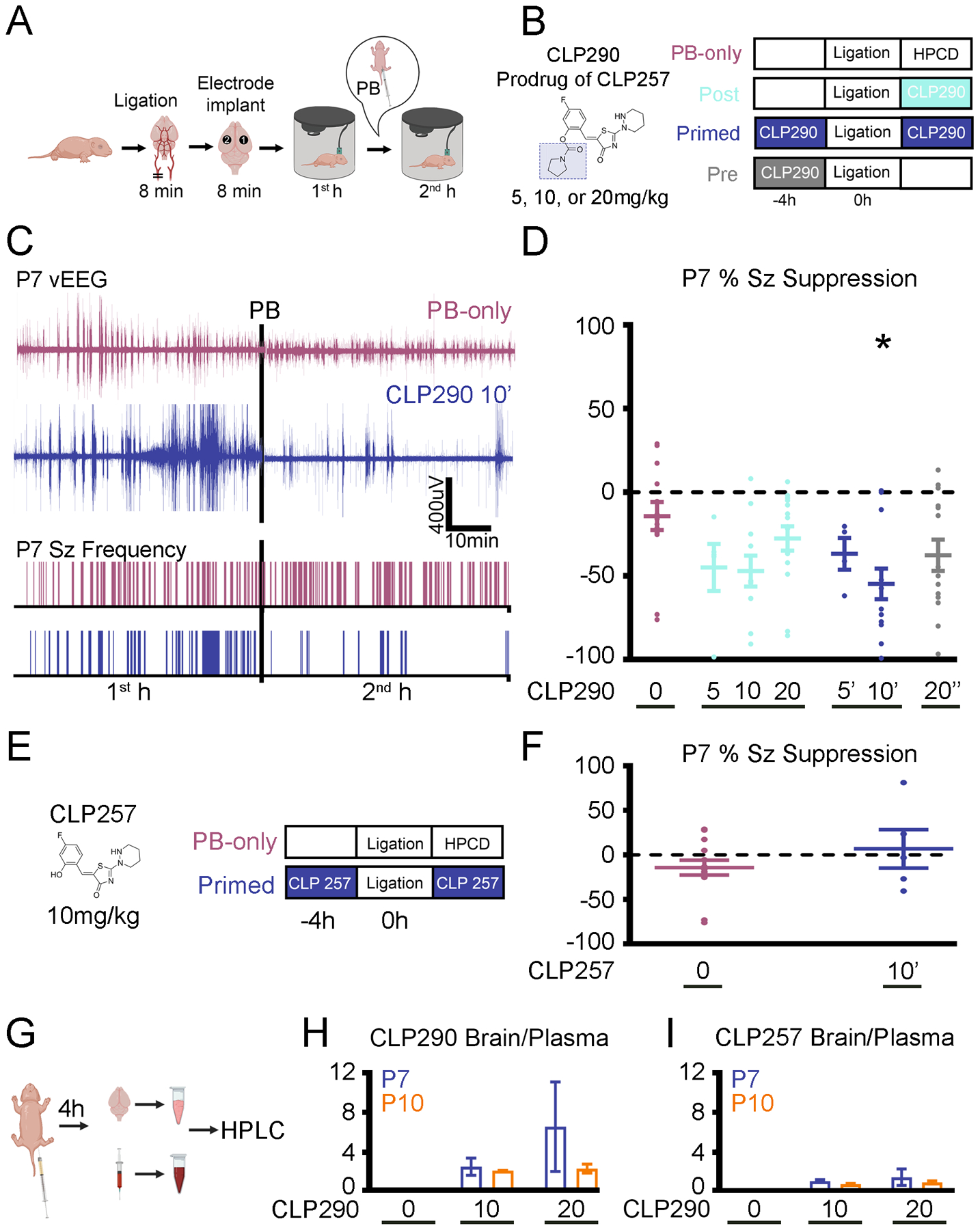
(A) Experimental design of a P7 CD-1 mouse model of ischemic neonatal seizures with continuous vEEG. Unilateral carotid ligation without transection, marking where the recording (“1”) and reference (“2”) electrodes were placed over bilateral parietal cortices with a ground electrode over the rostrum. (B) Doses and treatment protocols for CLP290 experiments. The prodrug’s full structure and that of CLP257 (shaded portion) is shown for reference. Post treatment groups (treated immediately after ligation) are denoted with the dose, such as 10. Pre-treatment groups (treated 4 hours before ligation) are denoted with (“) and primed (treated 4 hours before ligation and immediately after ligation) with (‘) alongside the dose administered, such as 20” and 10’. HPCD, 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (CLP257/290 dissolving vehicle). (C) Representative EEG traces and seizure (Sz) frequency raster plots of a PB-only and a 10 mg/kg CLP290 pre- and post–treated (“primed”; 10’) pup. Black bars represent the point of PB administration (25mg/kg; i.p.). (D) Analysis of EEGs represented and described in (C), assessing percent suppression of first- (1st) and second (2nd)-hour seizures after unilateral carotid ligation in P7 pups. *P<0.05 by one-way ANOVA vs. PB-only. PB-only group, n=14 pups; CLP290 groups, n=5 to 15 pups. Associated seizure burden and ictal events are shown in figure S1. (E) As in (B), for CLP257 experiments. (F) As described in (D), by CLP257 in a 10 mg/kg primed protocol. Data are from n=5 pups each. Note that the PB-only “0” data are the same as shown for comparison the CLP290-treatment groups in panel (D); groups assessed simultaneously. (G) Experimental paradigm to investigate the pharmacokinetic profile of CLP290 and CLP257. For characteristic peaks of CLP290 and CLP257 on HPLC, see fig. S2. (H and I) Brain to plasma ratio of CLP290 (H) or CLP257 (I) after i.p. administration. n=2 pups per group. Plots show all data points with means ± SEM. *P<0.05; two-way ANOVA.
