Fig. 3. CLP290-mediated regression of epileptogenesis detected using a PTZ challenge.
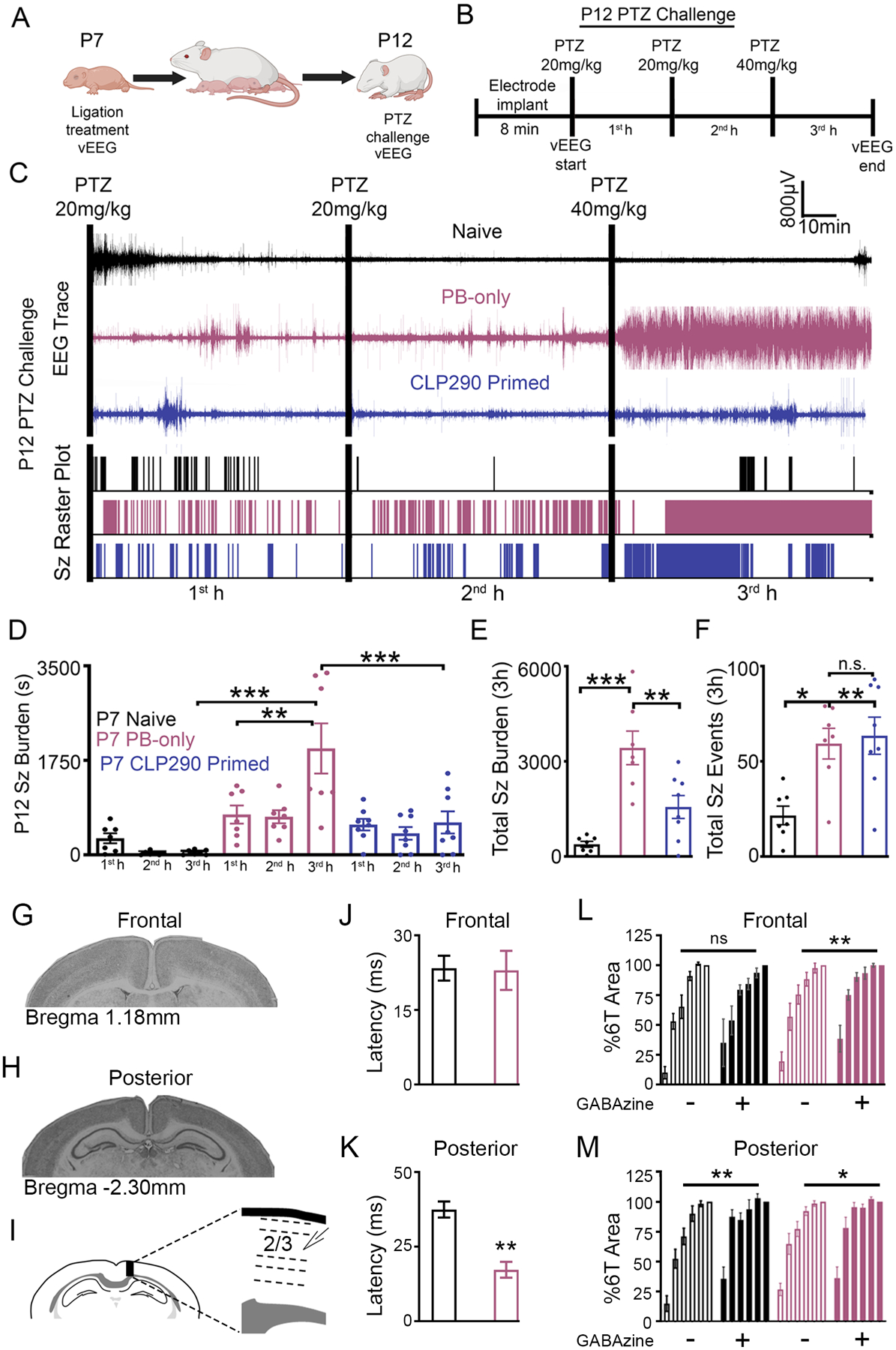
(A) Schematic to investigate the developmental benefits of CLP290 10’ treatment for P7 ischemic seizures. (B) P12 pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) challenge to evaluate epileptogenesis. (C) Representative EEG traces and seizure frequency raster plots for P12 pups that were untreated (naïve) or underwent PB-only or CLP290 10’ treatment at P7. Black bars indicate intraperitoneal PTZ injections. (D) 1st-, 2nd-, and 3rd-hour seizure burdens at P12 in CD-1 mice after PTZ injections. (E) Total electrographic seizure burdens over the three hours of vEEG recording. (F) Total seizure events over three hours of vEEG recording. Data plots show all data points with means ±SEM. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 by 2-way ANOVA. Naïve n=7; PB-only n=7; CLP290 10’ n=8 mice. (G to I) Representative coronal sections from frontal (G) and posterior (H) recording areas; line diagram (I) shows the placement of the recording electrode in an intact cortical column from a posterior section. (J and K) Mean 1T latencies from frontal (J) and posterior (K) sections from P12-P15 pups that were untreated (naïve) or PB-treated at P7. (L) Percent 6T area from frontal (L) and posterior (M) sections with and without GABAzine (1 μM). **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 by t-test and 2-way ANOVA. Naïve n=7, and PB-only n=14 mice.
