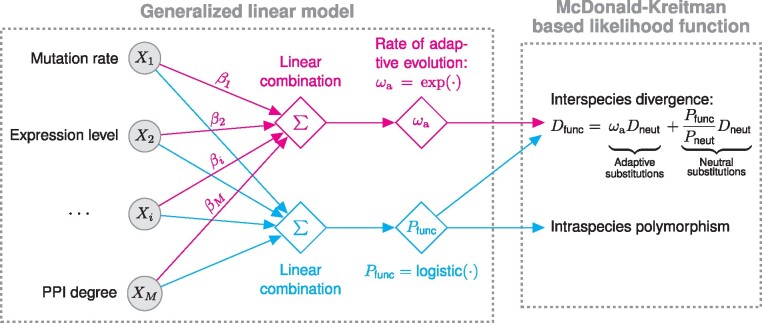
Fig. 1.
Schematic of the MK regression. The MK regression consists of two components: a generalized linear model and a McDonald–Kreitman-based likelihood function. First, I assume that, in a site-wise manner, the rate of adaptive evolution () at a functional site is a linear combination of local genomic features followed by an exponential transformation, in which regression coefficient βi indicates the effect of the ith feature on adaptive evolution. Similarly, I assume that the probability of observing a SNP () at the same functional site is another linear combination of the same set of genomic features, followed by a logistic transformation. Second, in the McDonald–Kreitman-based likelihood function, I combine and at every functional site with two neutral parameters, and , to calculate the probability of observed divergence and polymorphism data given model parameters. and denote the expected number of substitutions and the probability of observing a SNP at a neutral site, respectively. denotes the expected number of substitutions at a functional site.