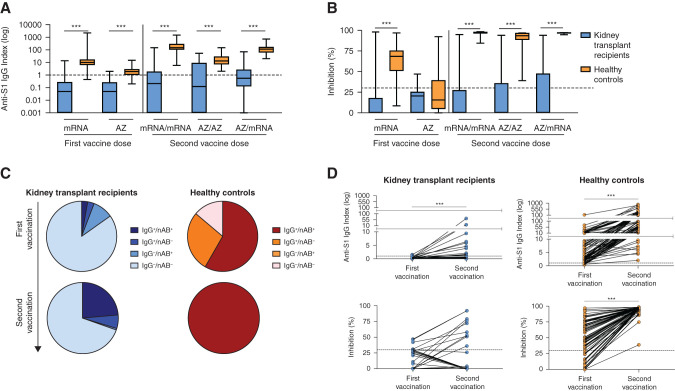
Figure 2.
Antispike 1 (anti-S1) IgG antibodies and neutralizing antibodies in kidney transplant recipients and healthy controls with different SARS-CoV-2 two-dose vaccination regimens. (A) SARS-CoV-2 anti-S1 IgG antibodies were determined by a chemiluminescent immunoassay and are represented logarithmically as an anti-S1 IgG index in kidney transplant recipients and healthy controls with different vaccination regimens. The black dashed line represents the cutoff for detection. A semiquantitative index of greater than or equal to one was classified as positive. (B) The neutralizing capacity of antibodies (nAB) against SARS-CoV-2 was determined by a surrogate virus neutralization test in kidney transplant recipients and healthy controls with different two-dose vaccination regimens. A cutoff of ≥30% binding inhibition was applied according to the manufacturer’s instruction to define positivity. The black dashed line represents the cutoff for detection. (C) Pie charts show the distribution of positivity for anti-S1 IgG and neutralizing antibodies determined by the surrogate virus neutralization test for all kidney transplant recipients and healthy controls after first and second vaccinations. Some individuals had antibodies with neutralizing surrogate activity but no detectable anti-S1 IgG antibodies. This could be due to the presence of antibodies of different isotypes and also due to the independent validation of the two tests, resulting in different cutoffs for detection. (D) Courses of anti-S1 IgG antibodies and nAB measured by the surrogate virus neutralization test are shown for 36 kidney transplant recipients and 83 healthy controls with available sera after both first and second vaccinations. The black dashed lines represent the cutoff for detection for anti-S1 IgG and nAB, respectively. ***P<0.001.