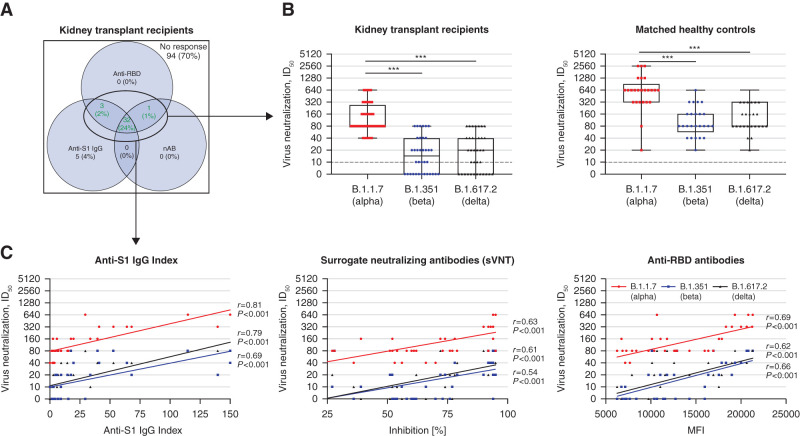
Figure 3.
Neutralization of the variants of concern B.1.1.7 (α), B.1.351 (β), and B.1.617.2 (δ) in VeroE6 cells in all 36 seroconverted kidney transplant recipients and 25 healthy controls after two-dose vaccination against SARS-CoV-2. (A) The positivity of anti-S1 IgG index (chemiluminescent immunoassay), surrogate neutralizing antibodies (surrogate virus neutralization assay; nAB), and antireceptor-binding domain (anti-RBD) antibodies (multiplex bead-based assay) is shown in a color-coded Venn diagram for all 135 kidney transplant recipients after two-dose vaccination. Seroconversion was defined if at least two of the following antibodies were detectable: anti-S1 IgG, nAB, or anti-RBD IgG antibodies. Neutralization activity against variants of concern in VeroE6 cells was performed in 36 seroconverted kidney transplant recipients, represented in the Venn diagram by the green numbers. (B) Neutralizing activity against the variants of concern B.1.1.7 (α), B.1.351 (β), and B.1.617.2 (δ) was determined in a SARS-CoV-2 infection assay using VeroE6 target cells and serial two-fold dilutions of sera from all 36 kidney transplant recipients with seroconversion and 25 matched healthy controls after two-dose SARS-CoV-2 vaccination. The black dashed lines represent the cutoff for detection. (C) The correlation between anti-S1 IgG index (left panel), neutralizing SARS-CoV-2 antibodies measured by a surrogate virus neutralization test (center panel), and anti-RBD antibodies (right panel) with the neutralizing activity of the different variants of concern B.1.1.7 (α), B.1.351 (β), and B.1.617.2 (δ) in kidney transplant recipients was evaluated by Spearman correlation analysis. ID50, serum dilution that reduces infection of cells by 50%. ***P<0.001. sVNT, surrogate neutralizing antibodies.