Figure 5.
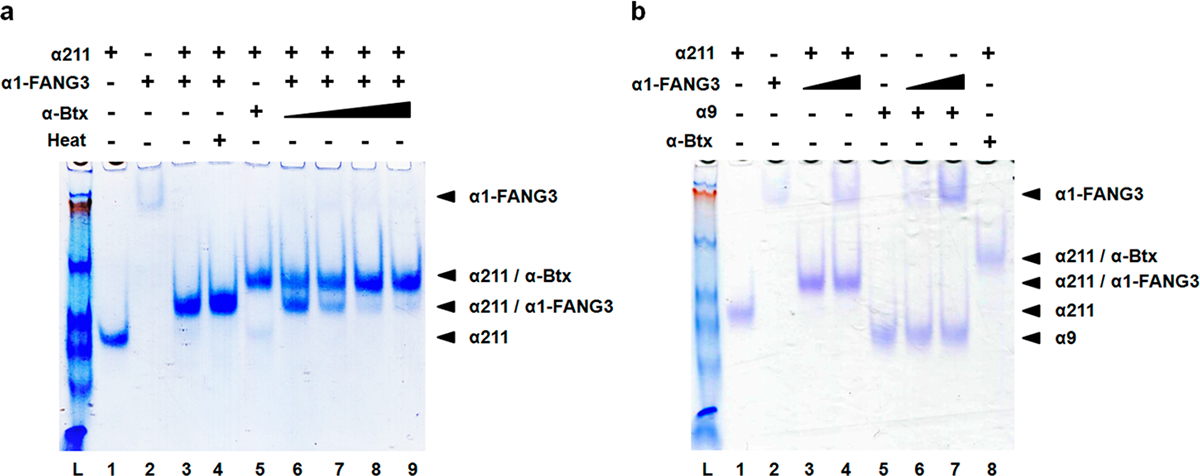
Native gel assays show α1-FANG3 binds α211 in solution. (a) Assay of binding of α1-FANG3 and α-Btx to α211. The α211:α-Btx and α211:α1-FANG3 ratios are 1:1 except in lanes 6–9 [α211:α-Btx:α1-FANG3 ratios of 1:1:1 (lane 6), 1:2:1 (lane 7), 1:5:1 (lane 8), and 1:10:1 (lane 9)]. α211 (lane 1), α1-FANG3 (lane 2), and their complex (lane 3) show distinct mobilities under native gel conditions. Heating at 37 °C for 30 min does not affect the α211/α1-FANG3 complex (compare lanes 3 and 4). The α211/α-Btx complex (lane 5) can also be distinguished from the α211/α1-FANG3 complex on the gel. In direct competition for binding to α211, a 1:1 α-Btx:α1-FANG3 ratio gives a gel shift that corresponds to both the α211/α1-FANG3 complex and the α211/α-Btx complex (lane 6). Increasing the α-Btx:α1-FANG ratio upon co-incubation with α211 decreases the intensity of the α211/α1-FANG3 complex band and increases the intensity of the α211/α-Btx complex band (compare lanes 7–9). (b) α1-FANG3 binds α211 specifically with no binding to related family member α9. The α1-FANG3:α9 and α1-FANG3:α211 ratios are 1:1, except in lanes 4 and 7 (2:1). α9 (lane 5) shows no complex with α1-FANG3 (lane 6), while distinct mobilities for α211 (lane 1), α1-FANG3 (lane 2), and their complex (lane 3) as seen in panel a remain.
