Figure 1.
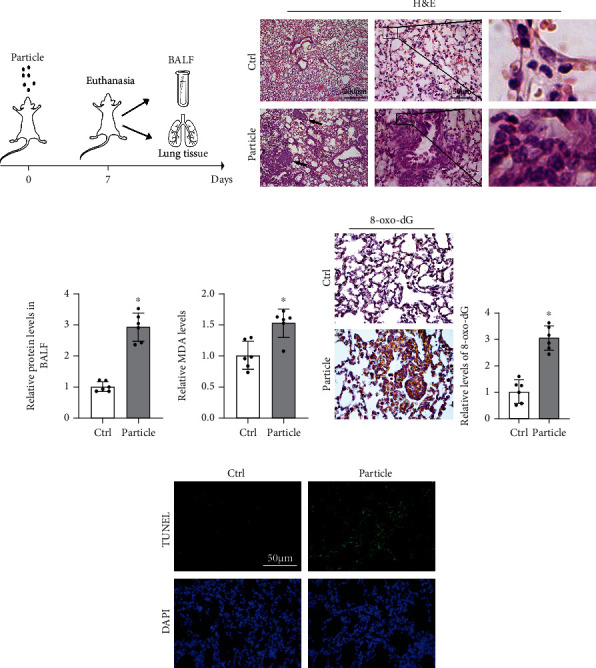
Particle caused severe oxidative injury in lung tissue. (a) Pattern of mouse model procedure. Mice received particles intratracheally at day 0 and sacrificed at 7th day. BALF and lung tissue were harvested for next analysis. (b) Representative H&E-stained lung sections (n = 6, black arrows indicated pulmonary nodule, and infiltration of inflammatory cells was magnified at right panel). (c) The protein content of BALF was measured. Results were shown as means ± SD (n = 6, ∗P < 0.05, Ctrl vs. particle). (d) Relative values of MDA in lung tissue from each group were measured. Results were expressed as means ± SD (n = 6, ∗P < 0.05, Ctrl vs. particle). (e) IHC staining of 8-oxo-dG in the lung tissue from the indicated group was performed and quantified. Representative images from each group were shown. Results were expressed as means ± SD (n = 6, ∗P < 0.05, Ctrl vs. particle). (f) Representative images of TUNEL assay staining in lung tissue from each group were shown.
