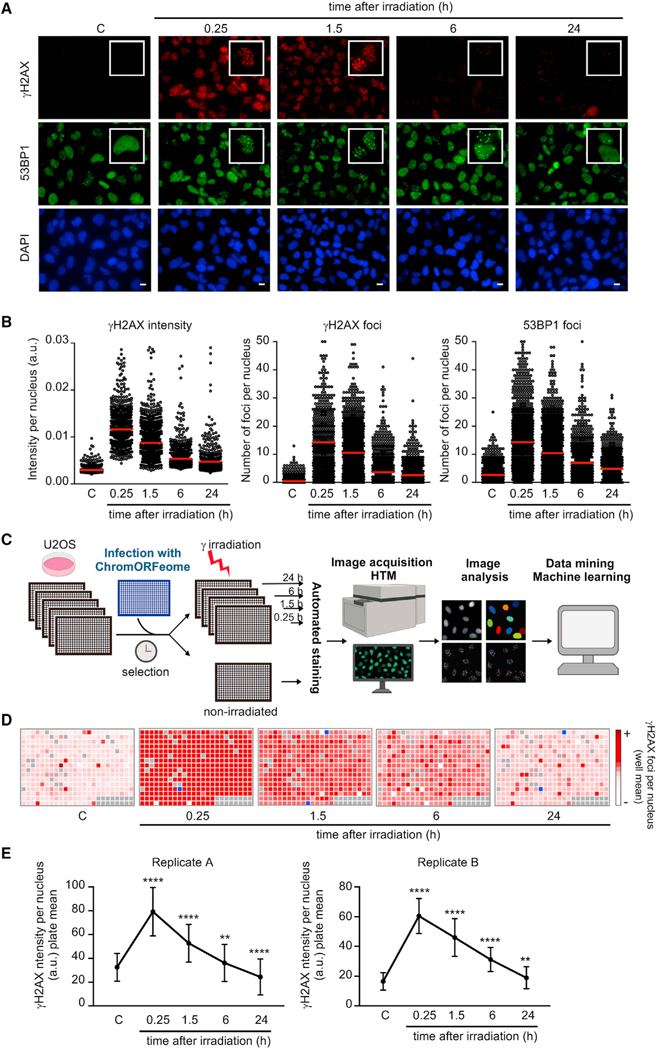
Figure 1. A high content screen for assessing chromatin regulation of DNA repair.
(A and B) Proof-of-concept high-throughput microscopy (HTM) assay for kinetics of DNA repair. (A) Accumulation of DNA damage response (DDR) proteins at DNA breaks in nuclei of U2OS cells after exposure to gamma irradiation (3 Gy) and recovery for the indicated times. Representative examples from the HTM images of immunostaining for γH2AX (red) and 53BP1 (green). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 10 μm. (B) HTM-mediated quantification of the kinetics of the DDR. Relative intensity of γH2AX staining per nucleus, number of γH2AX foci per nucleus, and number of 53BP1 foci per nucleus were determined in U2OS cells at the indicated times after DNA damage (3 Gy). Red bars represent the mean.
(C) Schematic of the ChromORFeome HCS for DNA repair.
(D) Diagram showing the kinetics of nuclear γH2AX foci in cells expressing individual ORFs in the ChromORFeome HCS (each well contains a particular ORF-expressing cell line). γH2AX foci number at each well and time point was obtained by getting the average of γH2AX foci per nucleus for all the nuclei in that well, and it is displayed with a color code. In gray, ChromORFeome control wells; in blue, empty wells. These are the results of a single experiment.
(E) Kinetics of nuclear γH2AX intensity in the two ChromORFeome HCS for DNA repair performed (replicate A and replicate B). The collection of all ORF-expressing cells in the ChromORFeome follow the expected kinetics of DNA repair. Nuclear γH2AX intensity for the entire ChromORFeome library-expressing cells was obtained by calculating nuclear γH2AX intensities for cells expressing individual ORFs of the library at each time point (mean ± SD; **p < 0.01; ****p < 0.0001 by one-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons, for each time point vs. non-irradiated control).