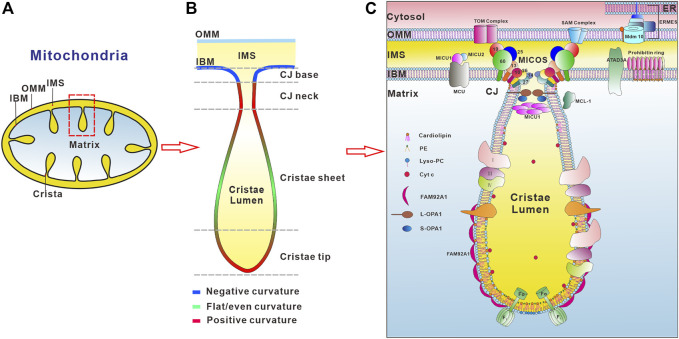
FIGURE 1.
Regulators involved in the organization of mitochondrial inner membrane curvature. (A) Schematic presentation of mitochondrial membrane ultrastructure and subcompartments. The outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM) and inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) delineate two aqueous compartments, the intermembrane space (IMS) (yellow color) between the OMM and the IMM, and the matrix (light blue), which is the innermost compartment. The IMM is further divided into the inner boundary membrane (IBM) and cristae membrane. (B) Schematic illustration of membrane curvatures at distinct regions of the cristae membrane. Positive membrane curvature is indicated in red color, negative curvature in blue, and regions with both or no apparent curvature are colored in green. (C) Factors involved in the regulation of IMM morphology. F1Fo-ATP synthase plays an important role in the formation of positive membrane curvature at the crista tip. The conical cardiolipin and PE reside in the inner leaflet of crista tip membrane while inverted conical lipid such as lysoPC locates in the outer leaflet of the lipid bilayer to maintain the positive membrane curvature at the crista tip. The MICOS complex consists of eight subunits, Mic10, Mic13, Mic14, Mic19, Mic25, MicC26, Mic27 and Mic60, residing in the crista junctions (CJs) (only the numbers are depicted in the figure for the ease of legibility). MICOS is required for the CJs and the contacts between the inner and outer membranes via interaction with the SAM (sorting and assembly machinery) complex. OPA1 is also enriched at the CJs. Interactions between membrane-bound long (L-) and soluble short (S-) forms of OPA1 are required to maintain the width of the CJs. MICU1 exclusively localizes at the crista junctions and binds to the IMM through electrostatic interactions. MICU1 contributes to the structural integrity of the CJ through formation of hexamers. The maintenance of CJ ultrastructure restricts the cytochrome C (Cyt c) inside the crista lumen region. The BAR domain protein FAM92A1 preferentially interacts with the negatively charged phospholipid cardiolipin, and plays crucial role in the formation of positive cristae membrane curvature. In addition, prohibitin ring and ATAD3A localizing in the IBM, and MCL-1 in the IMM and matrix, are also involved in the organization of the IMM.