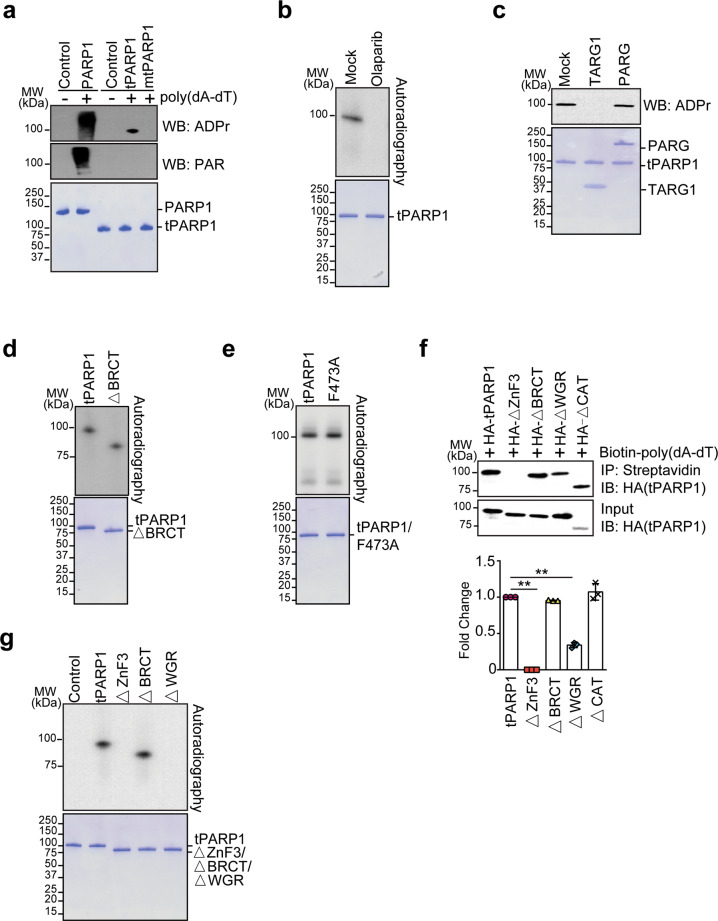
Fig. 4. tPARP1 catalyzes ADP-ribosylation.
a In vitro auto-ADP-ribosylation of PARP1 and tPARP1. Recombinant PARP1 or tPARP1 was incubated with NAD+ and poly(dA-dT). Auto-ADP-ribosylation was detected by anti-pan ADPr (upper panel) or anti-PAR (middle panel). Recombinant protein in each reaction was also examined by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining (lower panel). b Olaparib suppresses auto-ADP-ribosylation of tPARP1. c TARG1 but not PARG removes the auto-ADP-ribosylation of tPARP1. d, e The BRCT domain is not required for the auto-ADP-ribosylation of tPARP1. f HA-tagged full length of tPARP1 and four truncation mutants of tPARP1 were expressed in U2OS-PARP1 knockout cells, respectively. The cell lysates were extracted, followed by incubation with 5’ biotin-labeled poly(dA-dT). A streptavidin pull-down assay was performed and the complex was detected by western blotting (upper panel). Quantitative analysis of the levels of the pulled down proteins is shown in the lower panel. g The ZnF3 and the WGR domains are required for the auto-ADP-ribosylation of tPARP1. Data are represented as means ± SD as indicated from three independent experiments. Significance of differences was evaluated by Student’s t-test. **P < 0.01.