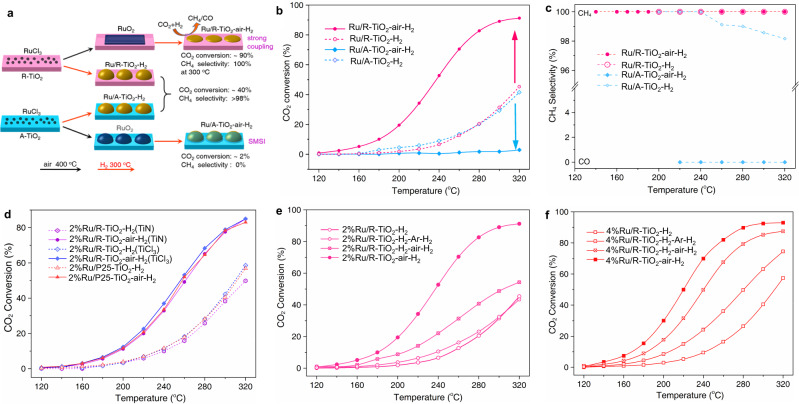
Fig. 1. Opposite catalytic performances of Ru/TiO2 supported on rutile (R–TiO2) and anatase (A–TiO2) for CO2 hydrogenation.
a Summary scheme of varied activity and selectivity by direct H2 reduction and after annealing in air. Ru/TiO2–H2 refers to directly reduced catalysts by H2, while Ru/TiO2–air–H2 refers to catalysts by annealing in air at 400 °C and further reduction by H2. b Temperature-dependent CO2 conversions. c Temperature-dependent CH4 selectivity. d Temperature-dependent CO2 conversions of 2% Ru/R–TiO2 catalysts on other R–TiO2 supports that were prepared from TiN and TiCl3, and P25 TiO2. Temperature-dependent CO2 conversions by annealing (e) 2% Ru/R–TiO2–H2 and (f) 4% Ru/R–TiO2–H2 catalysts in Ar and air. Ru/R–TiO2–H2–air–H2 means the catalyst was first reduced by H2 at 300 °C, then annealed in air at 400 °C, and reduced with H2 at 300 °C again.