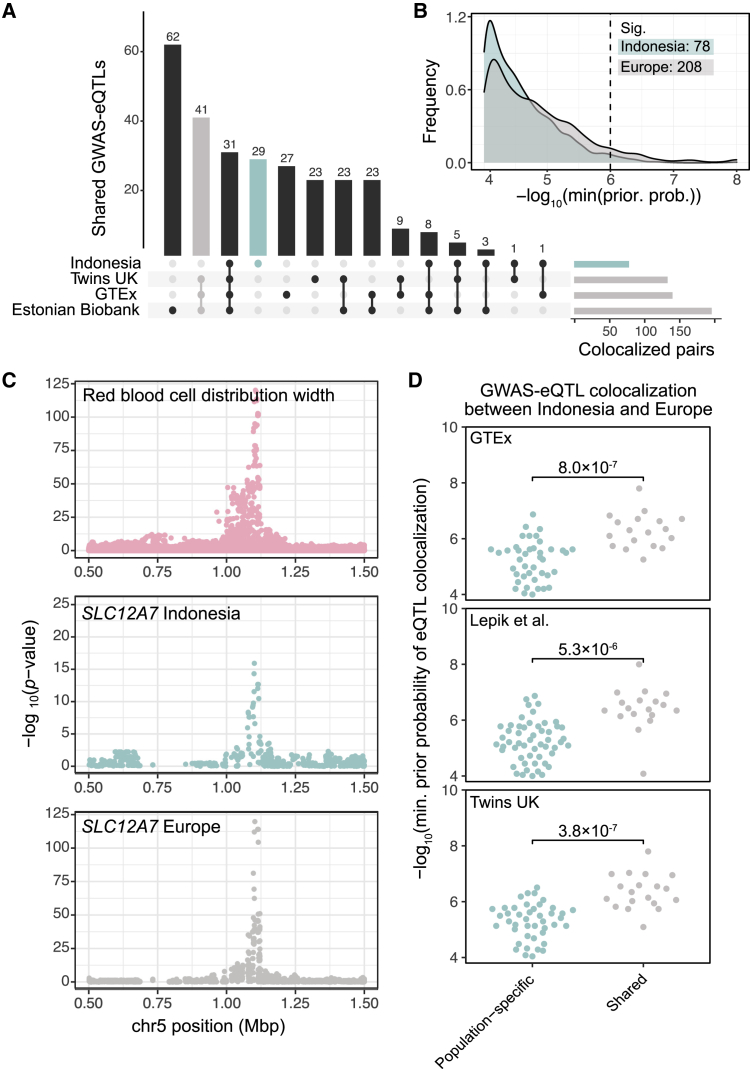
Figure 4.
GWAS colocalization with eQTLs from diverse populations identifies shared and population-specific variant-gene-trait associations
(A) Overlap of colocalized trait-gene pairs. The horizontal bar plot shows the numbers of significant colocalized pairs for each dataset. The dot plot shows the intersections and the vertical bar plot shows the numbers of shared trait-gene pairs for each intersection.
(B) European GWAS shows more colocalization with European eQTLs than Indonesian eQTLs. The x axis shows the −log10 of the lower bound of the prior probability of colocalization where the gene passes the colocalization threshold, and larger values indicate a more robust support for eQTL colocalization. The minimum prior probability threshold of 1.0 × 10−6 for robust colocalization is indicated.
(C) An example of a GWAS-eQTL significantly colocalized across Indonesia and all European datasets. −log10(p values) for red blood cell component distribution width (top), SLC12A7 eQTLs in Indonesia (middle), and SLC12A7 eQTLs in the three European datasets (bottom) are shown.
(D) Population-specific GWAS-colocalized eGenes are less likely to show eQTL colocalization between Indonesia and Europe than shared GWAS-genes. The y axis shows the −log10 of the lower bound of the prior probability of colocalization where the gene passes the colocalization threshold, and larger values indicate more robust support for eQTL colocalization.