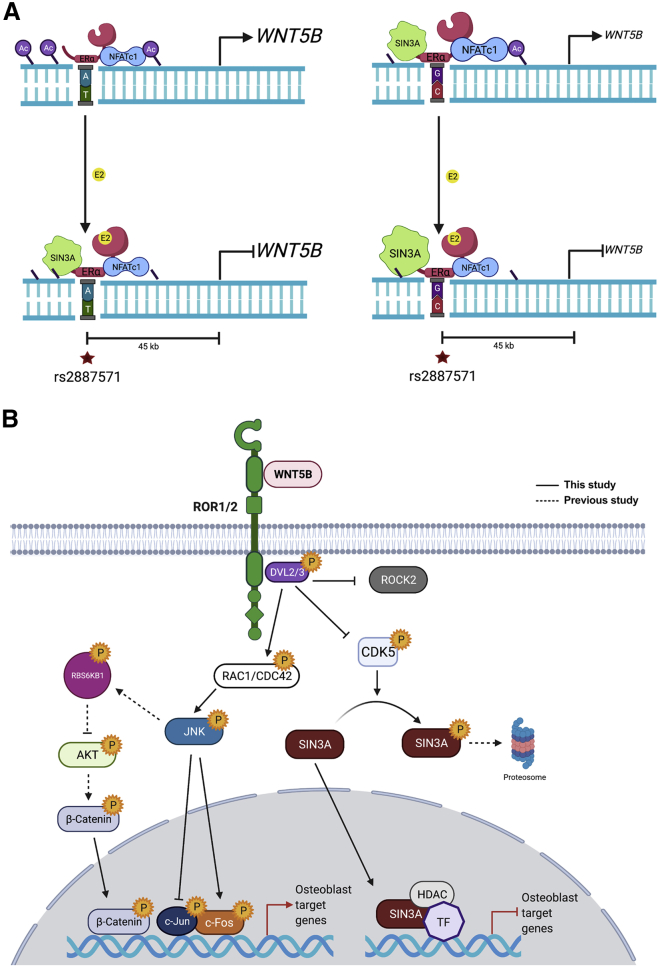
Figure 8.
Model of the regulation of WNT5B expression at SNP rs2887571 and the signaling pathway of WNT5B in osteoblasts
(A) The molecular mechanisms of ERα and NFATc1 at SNP rs2887571 in cells with homozygous AA (right) or homozygous GG (left) at rs2887571. (Top) Homozygous GG has increased ERα, NFATc1 and SIN3A compared to homozygous AA, which results in lower endogenous WNT5B expression due to the repressive effects of SIN3A. (Bottom) The presence of E2 recruits SIN3A to suppress the expression of WNT5B in both genotypes, with increased suppression in cells with GG due to increased recruitment of SIN3A.
(B) WNT5B binds with ROR1/2 then activates DVL2/3, RAC1/CDC42, p-JNK, and p-c-Fos. Phosphorylation of SIN3A by CDK5 results in proteasome degradation. WNT5B inhibits phosphorylation of CDK5 (Tyr15), resulting in accumulation of SIN3A. WNT5B also inhibits β-catenin activity in osteoblasts. Solid lines indicate the signaling pathways described in this study. The dashed line indicates the signaling that has been previously reported. P indicates phosphorylation. Created with BioRender.com