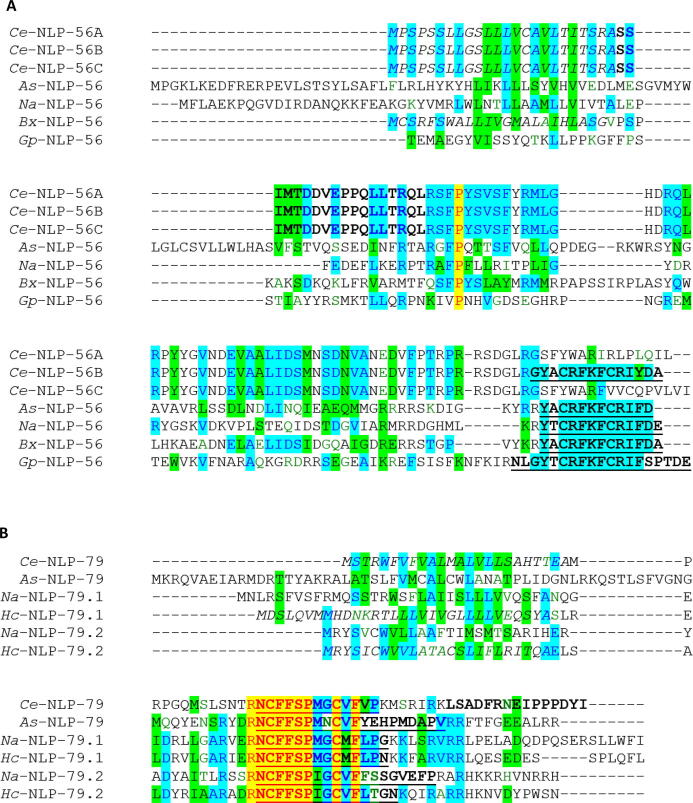
Fig. 1.
Novel predicted Caenorhabditis elegans neuropeptide-like proteins (Ce-NLPs) are conserved in parasitic nematodes. Multiple sequence alignments were performed using Vector NTI Advance 11.5 AlignX® (Lu and Moriyama, 2004). Text in italics highlights signal peptides as identified using Signal P 4.1 (Nielsen, 2017). Bold text indicates peptides predicted previously (see Van Bael et al., 2018). Bold underlined text indicates novel peptides predicted in this study based on their conservation in additional nematode species. Yellow and blue highlighted regions specify completely and partially conserved amino acid residues, respectively; green specifies similar residues. For all other novel NLP predictions made here (derived from nlp-8, -40, -48, -48, -52, -56, -58, -66, -67, -79 and -81 prepropeptide alignments) see Supplementary Table S5 and Supplementary Fig. S1. Ce, C. elegans; As, Ascaris suum; Na, Necator americanus; Hc, Haemonchus contortus; Bx, Bursaphelenchus xylophilius; Gp, Globodera pallida.