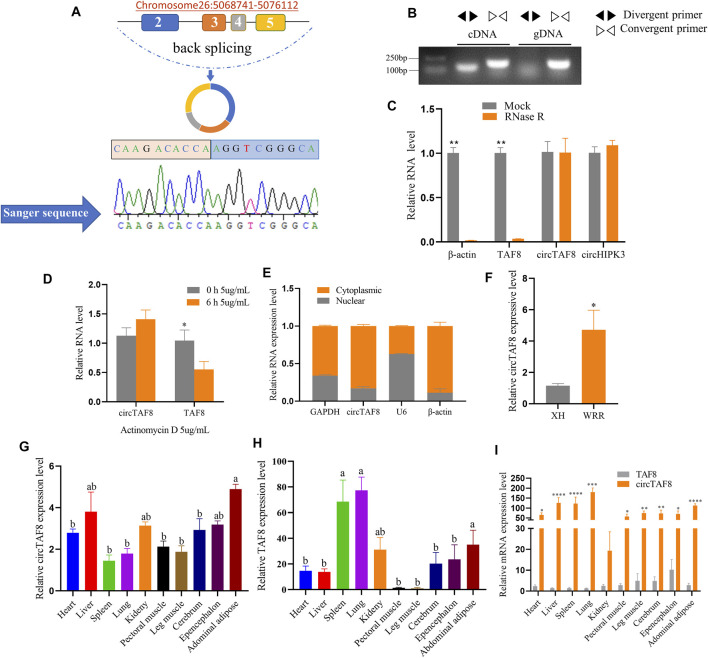
FIGURE 1.
Identification of circTAF8 in chicken. (A) Genomic location and looping model of circTAF8 and Sanger sequencing results. (B) Electrophoresis results of circTAF8 amplified from cDNA and gDNA with divergent and convergent primers, respectively. (C) Reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) assays to detect β-actin, TAF8, circTAF8, and circHIPK3 RNA expression levels with and without RNase R treatment. (D) RT-PCR to detect circTAF8 and TAF8 RNA expression levels with and without actinomycin D treatment. (E) RT-PCR results showing the circTAF8 subcellular localization. (F) RT-PCR results showing the circTAF8 expression level in XH and WRR groups. (G) Relative RNA expression level of circTAF8 in diverse tissues. (H) Relative TAF8 RNA levels in diverse tissues. (I) The relative levels of TAF8 RNA and circTAF8 in each tissue. The results of are shown as mean ± S.E.M from at least three biological replicates. The statistical significance of the differences was assessed using the unpaired Student’s t-test or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) (* p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; **** p < 0.0001).