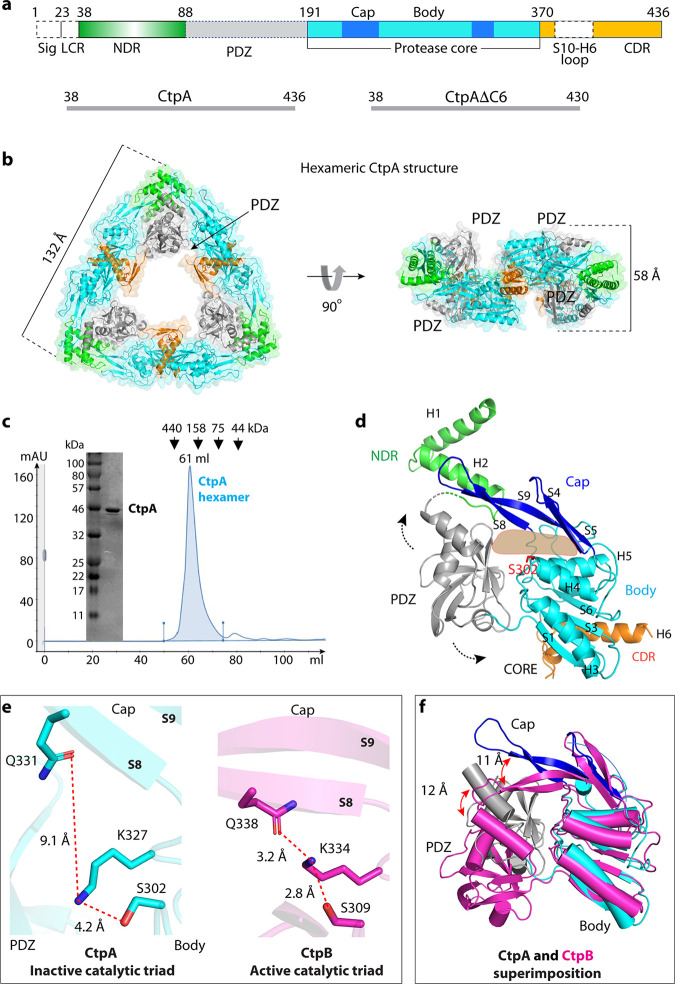
FIG 1.
Overall structure of CtpA. (a) Top: CtpA domain organization. The dashed lines indicate the disordered regions (PDZ and the S10-H6 connecting loop) that are not resolved in the crystal structure. NDR = N-terminal dimerization region; CDR = C-terminal dimerization region; Sig = signal sequence; LCR = low complexity region. The sequence ranges of the two CtpA constructs used this study are shown in the lower panels. (b) Cartoon and transparent surface views of CtpA hexamer. The domains are colored according to the depiction in panel a. (c) SDS-PAGE analysis and gel filtration profile of CtpA. mAU = milli-absorbance units; kDa = kiloDaltons. (d) A CtpA subunit in cartoon view. Secondary structural elements in CtpA are labeled, except in the PDZ domain. The two dashed arrows indicate the mobile PDZ domain in the CtpA hexamer. The light orange shape indicates the tunnel between the cap and the body region. (e) Comparison of the catalytic triads of P. aeruginosa CtpA and B. subtilis CtpB (PDB ID 4C2E). The S8 and S9 labels refer to β-strands 8 and 9 in the cap region. (f) Superposition of the core domains of inactive P. aeruginosa CtpA (cyan) and active B. subtilis CtpB (magenta). Catalytic Ser-302 in CtpA and Ser-309 in CtpB are in red sticks. Red arrows indicate the lifted-up (CtpA) and clamped-down positions (CtpB) of the PDZ and the cap subdomains.