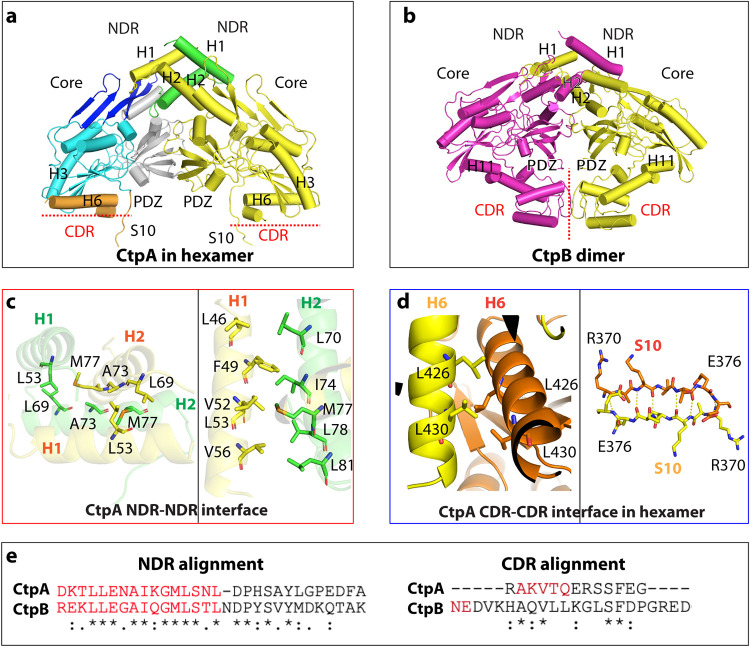
FIG 2.
Different oligomerization modes of P. aeruginosa CtpA and B. subtilis CtpB. (a) CtpA dimer extracted from the CtpA hexamer. (b) B. subtilis CtpB dimer (PDB ID 4C2E). CtpB H11 is the equivalent of CtpA H6. (c) The N-terminal dimerization interface of CtpA involves hydrophobic interactions between two H2s (left) and between H1 and H2 (right). (d) The C-terminal dimerization interface of CtpA involves a short leucine zipper-like interaction between two H6 helices and antiparallel β-sheet formation between two S10s. (e) Alignment of the conserved NDR sequence and divergent CDR between P. aeruginosa CtpA and B. subtilis CtpB.