FIG 3.
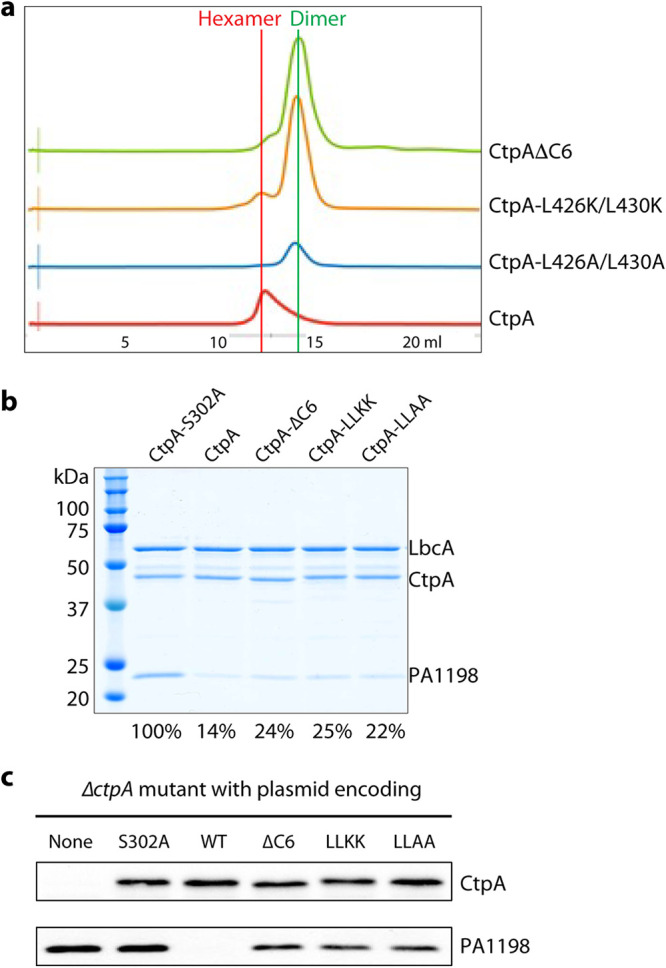
Full protease activity of CtpA requires C-terminal dimerization region. (a) Elution profiles of wild-type and mutant CtpA proteins. (b) Substrate degradation assay in vitro. His6-PA1198 served as the substrate for the assay. Gels from a single experiment are shown, but the amount of PA1198 degradation is the average from two independent experiments, determined as described in the Materials and Methods section. The number below each lane is the percentage of remaining PA1198 after 3 h, relative to the first lane using the inactive CtpA. (c) Substrate degradation in vivo. Plasmid-encoded protease-dead CtpA(S302A), wild type (WT), ΔC6, L426K/L430K (LLKK), and L426A/L430A (LLAA) were produced in a P. aeruginosa ΔctpA strain. None = empty plasmid vector control. The CtpA proteins and accumulation of the PA1198 substrate were detected by immunoblot analysis with polyclonal antisera.
