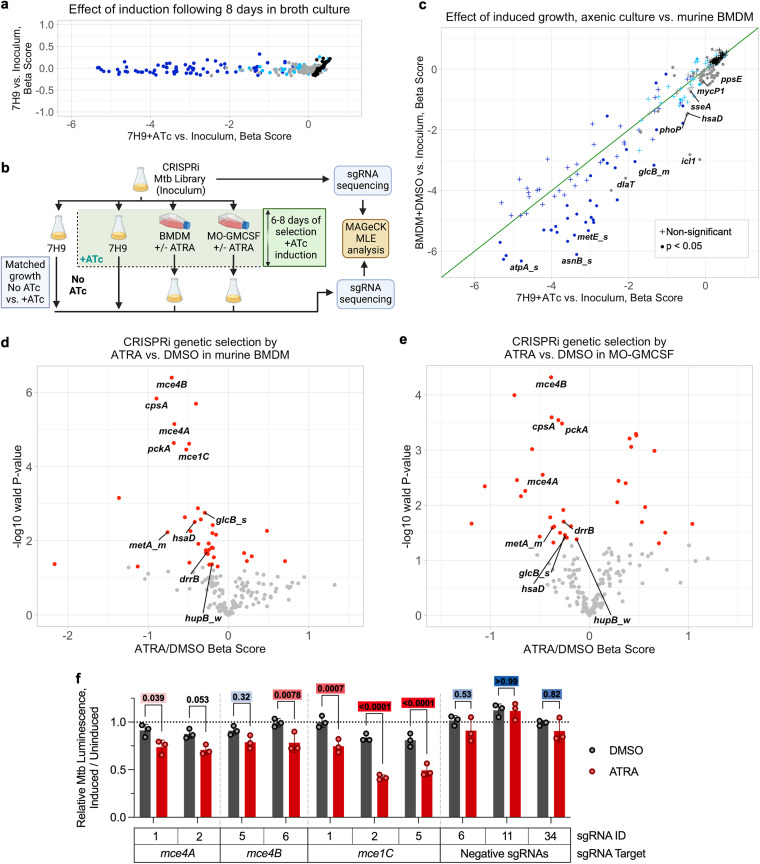
FIG 3.
Bacterial CRISPRi reveals increased reliance of M. tuberculosis on lipid import genes in macrophages treated with all-trans-retinoic acid. (a) Changes in gene-sgRNA set representation as measured by beta score (similar to log fold change), following CRISPRi library induction (+ATc) in axenic medium compared to the score for uninduced growth. Dark-blue points represent essential genes targeted with sets of strong (_s) or medium (_m) hypomorph sgRNAs (3 sgRNAs per point), light-blue points represent essential genes targeted with weak (_w) hypomorph sets of sgRNAs (3 sgRNAs per point), gray points represent nonessential genes, and black points represent individual negative (nontargeting) sgRNAs. (b) Schematic of CRISPRi experiments in macrophages and axenic broth culture. (c) Changes in gene-sgRNA set representation as measured by the beta score following CRISPRi library induction in axenic medium compared to the score for induced (+ATc) growth in primary mouse macrophages. Significance is measured by determining the Wald P value (equivalent to an adjusted P value). Point colors are as described for panel a; the green line is at the diagonal. (d, e) Volcano plots showing changes in gene-sgRNA set representation between 5 μM ATRA- and DMSO-treated primary macrophages from mouse (d) and human (e) (MO-GMCSF) sources. Red points represent gene-sgRNA sets that are significant at a Wald P value cutoff of <0.05. (f) MO-GMCSF control of autobioluminescent single-sgRNA clonal strains of Mtb at 5.5 days following infection and treatment with 5 μM ATRA, comparing strains with ATc-induced knockdown of the indicated Mtb genes to the same strains with no knockdown. Statistics were performed using a 2-way ANOVA with Šídák’s multiple-comparison test; color-coded adjusted P values are shown above each comparison (red indicates a P of <0.05, white indicates a P of 0.05, and blue indicates a P of >0.05 [continuous scale]). Infections were performed at a multiplicity of infection of 1 bacterium (a to e) or 2 bacteria (f) per macrophage.