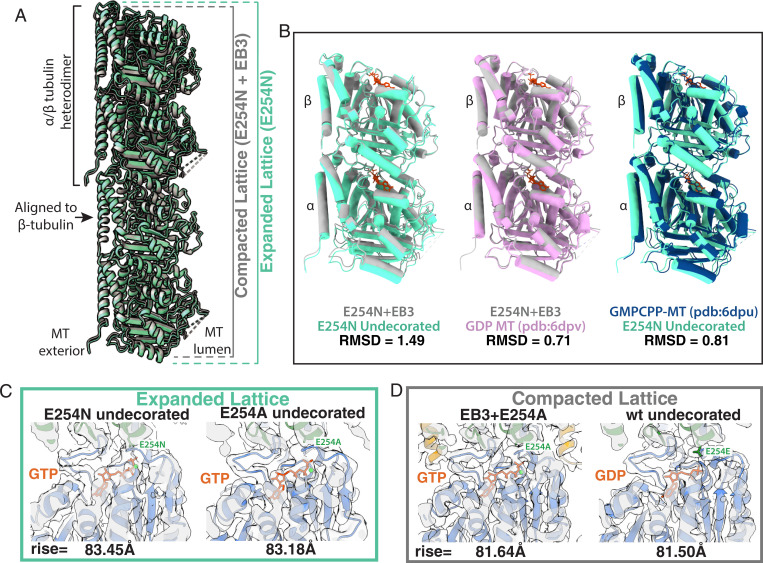
Fig. 4.
GTP state and compaction for wt, E254N, and E254A MTs. (A) Visualization of how the MT axial repeat changes, either through hydrolysis of GTP or through EB3 binding to catalytically inactive MTs. Specifically, the panel shows atomic models for the structures determined herein, with the undecorated E254N MT shown in green and E254N+EB3 MT in gray. (B) Comparison of tubulin heterodimers to show the structural changes that occur upon compaction. Dimers are aligned onto β-tubulin, which has been shown to undergo the least amount of conformational changes in previous studies and herein. RMSD values are reported below each comparison. (C) Expanded lattices, with a rise >83 Å and with clear GTP density. Shown here as examples of expanded lattices for undecorated E254N (3.8 Å) and undecorated E254A (3.4 Å) maps. (D) Compacted lattices with a rise <82 Å can be formed by EB3 binding (while maintaining GTP) or by hydrolysis into the GDP state. Examples for the compacted lattices observed are EB3+E254A (3.5 Å) and the undecorated wt lattice (3.8 Å).