Figure 3:
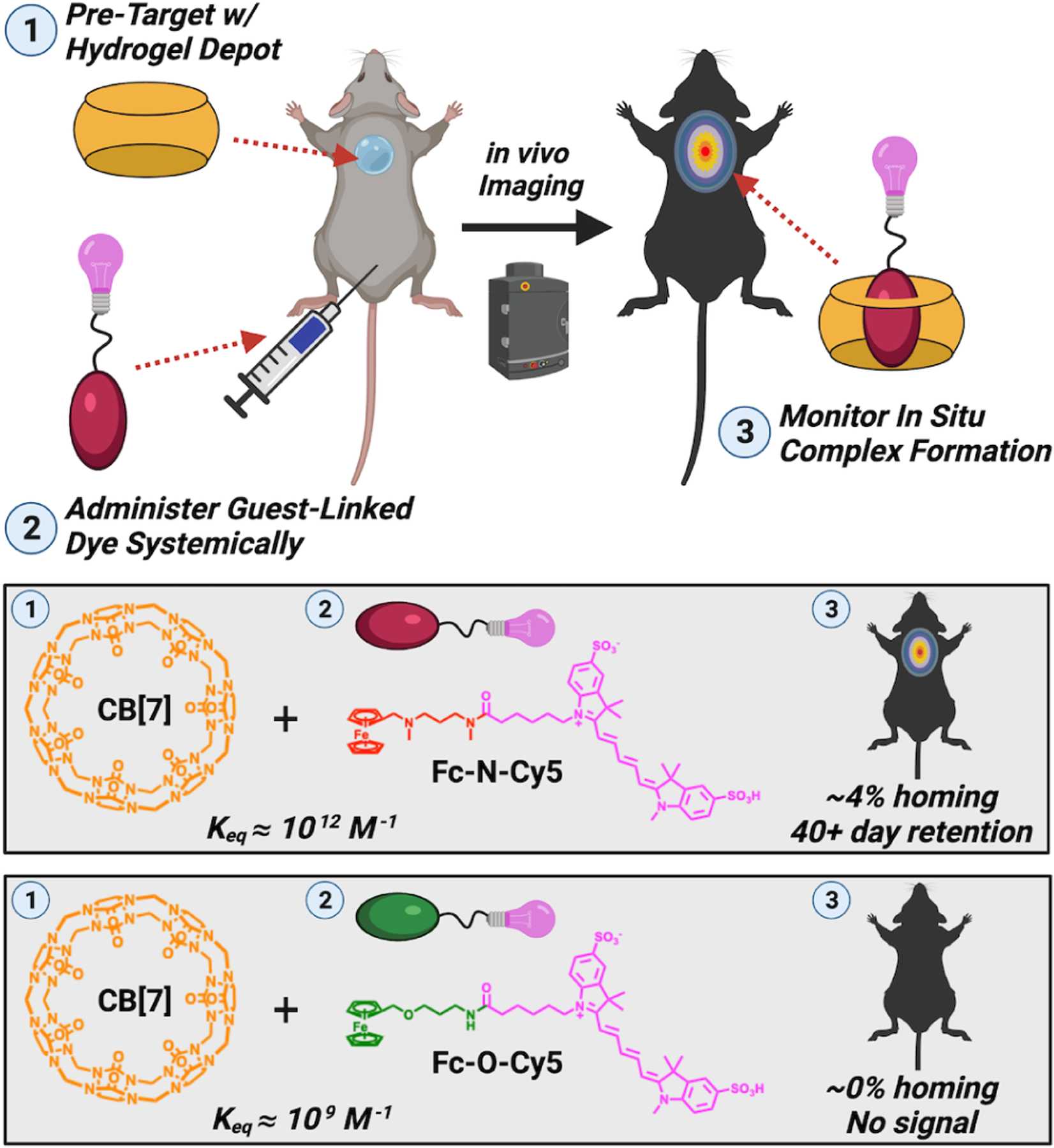
Methodology to assess the affinity needed for in situ recognition and targeting. A hydrogel presenting pendant CB[7] macrocycles was implanted locally at a site. Subsequently, a near-infrared fluorescent probe (Cy5) modified with two ferrocene guests having different affinities for CB[7] (Fc-N:1012 M−1 vs. Fc-O:109 M−1) was administered systemically. Through in vivo imaging, the amount of dye localized and retained at the site presenting CB[7] was then quantified. Subtle differences in the guest structure, altering their resulting affinity for CB[7], led to dramatic changes in the effectiveness of in situ complexation.
