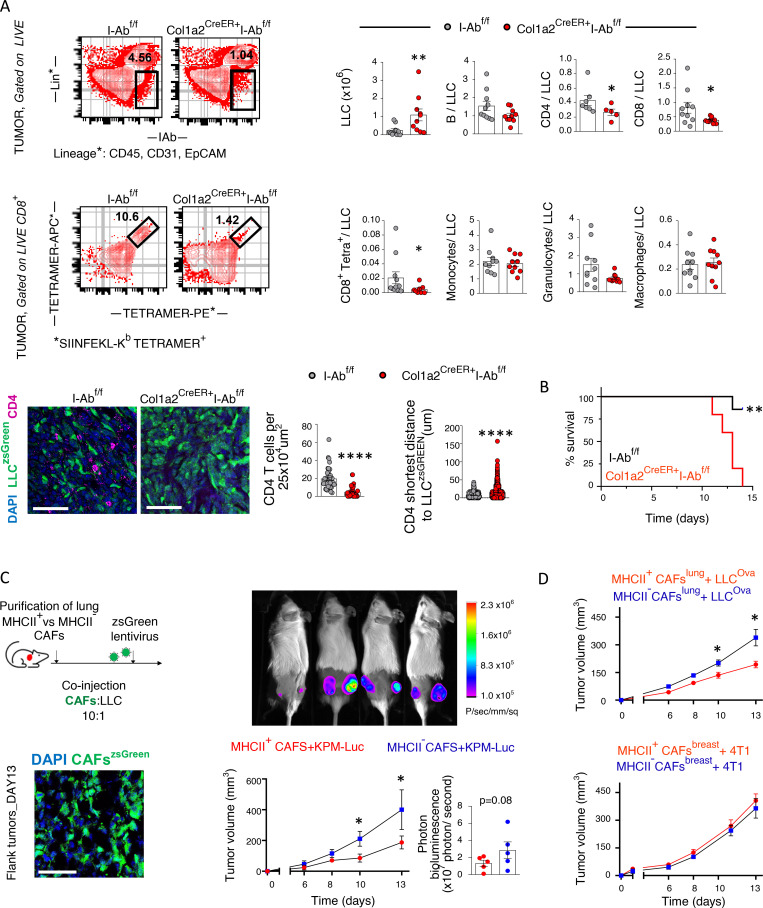
Figure 4.
Lung apCAFs restrict tumor growth via MHCII. (A) Top: Col1a2 CreER+I-Abfl/fl and I-Abfl/fl mice were inoculated with LLCmcherryOva or LLCzsGreen. Representative FACS plots of Lin−IAb+ and CD8+tetramer+ cells (gated as tetramer-APC+tetramer-PE+) in digested tumors. Cumulative data of tumor burden and intratumoral immune profiles (n = 3–7 per group, pooled from two experiments). Immune cell number was normalized to cancer cell number. Numbers of cancer cells (tumor burden) and immune cells were assessed by FACS using counting beads. Bottom: Representative immunofluorescence for CD4 and LLCzsGreen cells. Cell density of CD4+ T cells in tumors of Col1a2 CreER+I-Abfl/fl versus I-Abfl/fl mice (cells per 25 × 104 μm2 regions in whole-slide images). Shortest distance between CD4 and LLCzsGreen cells in tumors of Col1a2 CreER+I-Abfl/fl versus I-Abfl/fl mice (n = 2 or 3 mice per group). Samples were analyzed by confocal microscopy with a 20× objective. Bars, 50 µm. (B) Survival curves (representative of two experiments). (C) Left: Experimental scheme and immunofluorescence of subcutaneous tumors after cotransplantation of LLC cells plus zsGreen-expressing MHCII+ versus MHCII− CAFs into syngeneic mice. Samples were analyzed by confocal microscopy with a 20× objective. Bars, 50 µm. Right: Tumor growth after subcutaneous cotransplantation of luciferase-expressing KPM cells plus MHCII+ versus MHCII− CAFs in syngeneic mice (n = 5 mice per group). (D) Top: Tumor growth after subcutaneous cotransplantation of LLCmcherryOva cells plus lung tumor–derived MHCII+ versus MHCII− CAFs in syngeneic mice (C57BL/6; n = 6 mice per group, representative of two experiments). Bottom: Tumor growth after subcutaneous cotransplantation of 4T1 cells plus breast tumor–derived MHCII+ versus MHCII− CAFs in syngeneic mice (BALB/c; n = 8 mice per group, pooled from two experiments). (A–D) *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ****, P < 0.0001. Error bars, mean ± SEM; two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test.